by scott.gillum | Aug 10, 2012 | 2012, Marketing
In 2004, I was part of research project with a professor at the Kellogg School of Management and the CMO Council that sought to understand what CMO’s believed to be critical for their success. The most common response was a seat at the table with other senior executives.
Four years ago, I was part of another research effort focused on the CMO’s top priorities, and number one on the list was to be viewed by their peers as strategic thinkers. Finally, I believe the day has come for that to happen.
Marty Homlish, the CMO of HP believes the line between business and consumer marketing is disappearing. Homlish states, “ Behind every B-to-B company is a consumer. The way you communicate to that person is as an informed consumer.”
Technology has allowed work to follow us home and our home life to the office. It has blurred the line between our personal and business personas. The concept of being ‘at work’ is now more a state of mind rather than a physical location or particular time of day.
If business buyers – who were once thought of only as rational decision makers – now need to be communicated with as informed and emotional consumers who no longer fit our past perception of work hours and locations, what might this mean for the future of business-to-business marketing?
To answer that question, one must first understand the difference between how business and consumer marketing operate. According to a Booz & Co and the ANA in The New B2B Marketing Imperative study, B2B marketing has primarily taken an “inside out” approach, focused on the needs of the company and accounts rather than customers.
By contrast, 85% of B2C marketers, who take an “outside in” approach said they were involved in growth initiative decisions which are considered to be strategic such as new market entry, customer relationships and market driven product development.
Additionally, 42% of B2C marketers play a key role in building customer relationships, versus 8% of business marketers. B2B marketers said that “Customers are rarely driving the process and their input is seldom integrated from end to end.”
If today’s business buyers really are “educated consumers” as Homlish suggests, then business marketers can no longer be left out of customer and product conversations. It also means that organizations that target business buyers, who has given lip service to transitioning from being “product led” (inside out) to “customer focused” (outside in) now need to act. And the tip of the spear for driving that change – is marketing.
By better understanding and influencing the needs, desires and emotional drivers of individual business consumers, marketers will be in the strategic conversation and lead the transition. This is the key to unlocking the executive suite.
However, the organization is not just going to give marketers a seat at the table and there is a good possibility that executives don’t get it. As one of the marketing directors said in the study; “Marketing is just not in the DNA of senior management.” You will have to make it happen.
The study concludes that; “Core marketing capabilities – those that directly influence customers – have the highest correlation to market share growth.” Senior executives may not understand marketing but they do understand growth.

by scott.gillum | Aug 3, 2012 | 2010, Marketing
Original post date May 2010, the post was recognized as one of the best post on Social Media for 2010.
As with most new technologies, social media is starting to “settle in” and common applications of the platforms are becoming known. In many large B2B organizations, that means social media is finding a home in the marketing communications group, often landing in PR.
That seems fine for B2C organizations; however, I’m not convinced that it’s the right spot, and/or the only spot for social media in B2B companies.
The Upside Down Funnel
In most B2B organizations corporate marketing’s role is related to driving “top-of-the-funnel” activities. From advertising, PR, and now social media, the focus is on creating awareness…and hopefully, driving consideration and preference. There is another opportunity that may not be considered, a part of the funnel where marketing, in particular social media, can play a valuable role.
It’s at the very bottom of what I’ll refer to as the “upside down” funnel. To find such an opportunity you have to think about a funnel that starts with once a prospect becomes a customer.
Just as a sales funnel has stages so does the customer relationship management process. Companies should be actively pursuing strategies and tactics to retain, expand, grow and then leverage customer accounts to win business.
This is where I think the “sweetspot” is for social media in B2B. Here’s why: social media is about “consumers selling to consumers”, or “professional-to-professional.” If a company does its job of nurturing and retaining customers, it should be able to transition from having a relatively unknown prospect, to a known customer, to hopefully, a well-understood customer advocate…at least that’s the goal.
The Opportunity
If a company enables those customer advocates with social media it gives them a platform to spread the good word. The potential of this opportunity is huge, and for the most part, being missed at most companies today.
As we all know, word of mouth is the most effective marketing there is, enabling it with technology creates scale, and the ability to track it.
To do this successfully, companies have to first identify this opportunity within their organization; second, they have to change their current way of thinking about social media beyond its present use in marcomm and PR.
It means finding uses and opportunities within sales and customer service. Yes, listening to customers chat about your service on Twitter is important, but I’m talking about creative ways to use it for:
- customer-to-customer referrals & recommendations
- building communities
- facilitating discussion groups
The goal is to find ways to emotional connect avid customers to the company and/or products, and then provide them with an outlet to communicate that passion.
What to Do
As relationships deepen, customers begin interacting in more personal channels. Through those interactions they are likely to share more intimate details about themselves, and their relationship with products/services and the company.
Companies have to be able to collect this information across channels to create a complete profile of a customer. If this can be achieved, an organization will have everything it needs to begin enabling, influencing and studying customer advocates.
Finally, watch out for the “silo” effect. Typically, at least three different organizations will be interacting with the customer as the relationship develops. But it’s only one customer interfacing with what the customer expects to be one company. The organization has to be “in sync” because the last thing a company wants is to provide a customer with a platform for communicating the wrong message. Turning an advocate into an adversary is not the goal.
by scott.gillum | Aug 1, 2012 | 2010, Marketing
Original post date December 15, 2010
Last month I had the chance to be a panelist at a forum hosted by Wolfgang Jank and the Robert H. Smith School of Business at the University of Maryland. The topic was on Informatics – Data Driven Decision Making in Marketing.
Agreeing to participate without knowing what I would discuss, I searched my files reviewing old project work. Not only did I find a relevant effort, I also realized that I had spent two years working on building and implementing an insights program at a major Financial Services firm.
What’s interesting about the topic is that everyone will agree that they should be more data driven, or fact based, with their decision-making. Heads will nod when it’s discussed, it’s intuitive, and so the question…and the problem, is why doesn’t it happen?
The company I was working with had an abundance of data but were faced with two consistent problems related to the use of it:
- Reps wanted better insight
- Customers wanted a POV
The first issue we probably spent a good six months on defining what an ‘insight” was, how to create it, and who was responsible for doing it. The second issue was more complicated, and took much longer to resolve.
Over that two-year period, I learned how challenging it is for an organization to use one source of data effectively across the enterprise. Some of the challenges we uncovered were typical such as lack of resources, process, and funding. Others were more challenging: People funded their own resources and research to support their strategy, budget or group.
To begin to solve this complex problem we created a “data value chain” (see below). The starting point was having one centralized source for data. As we discovered, as data flows from across the organization to the customer, enhancements were needed to make it more valuable, like growth rings on a tree.
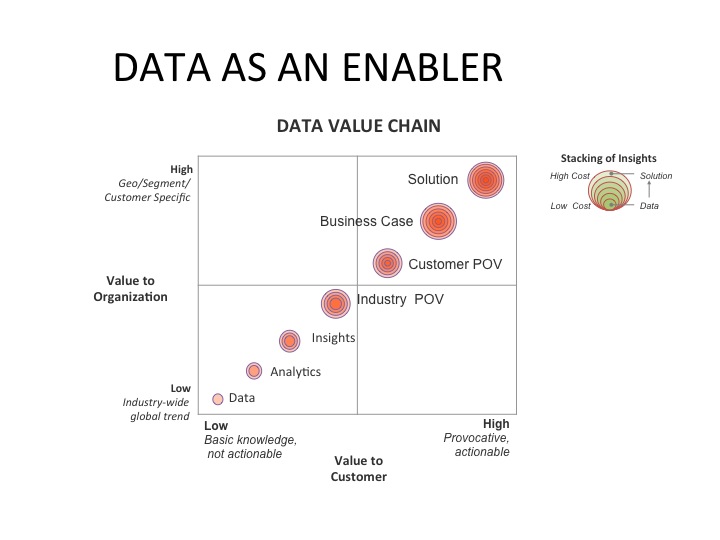
As data became more customized, and localized, it grew more valuable. This helped to identify why, for example, research that was being produced at corporate was not often used by the sales teams…it lacked relevancy, especially in regions outside of the US.
Once we got everyone on the same page the next challenge was to align the various groups in the organization across the value chain. We learned there could be as many as five different groups involved in handoffs as the data moved across the value chain. This help to explain why product groups were developing solutions without market insights, and regions were not leveraging corporate insights for business development.
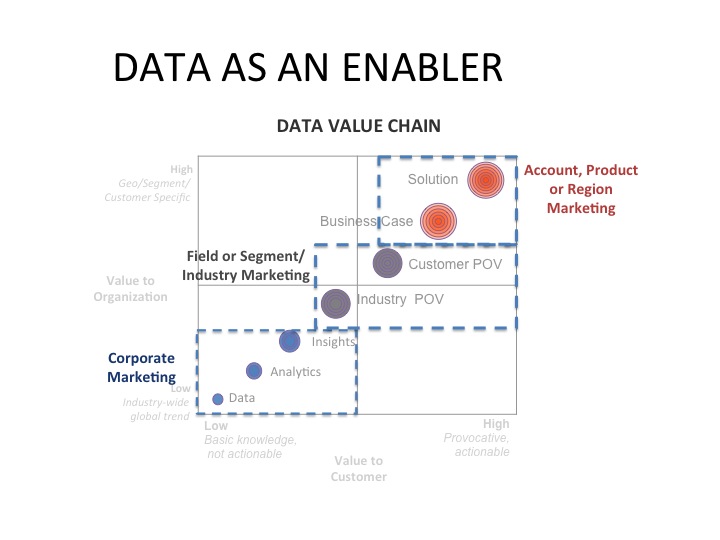
Handoff points in an organization
As a result, we had to design process maps, hand-off points, engagement process, etc. The elephant in the room, and one of the biggest challenges was wrestling with the budget. The solution for that last huddle was turned out to be pretty simple.
The corporate “insights” team would work with those regions that wanted to work with corporate. Those regions had to be willing to fund resources to finish the “last mile”…building a solution or a customer business cases with a defined solution in mind. Even though everyone wanted more relevant insight, and more defined points of view, not all regions were willing to pay for it. Finally, to secure the funding to make the fixes we had to be able to answer a very simple question; “how does being more data driven provide value to the organization?”
The answer was getting the data closer to revenue or a sale….”turning data into dollars.” The epiphany wasn’t that the value was found at the end of the chain but the number of groups, and the coordination needed to be involved to reach that destination.
by scott.gillum | Jul 30, 2012 | 2009, Marketing
Original post date July 16, 2009
I’m about to share with you the secret formula for; 1) creating a rock solid, compelling value proposition (for products, services, solutions, etc.) and, 2) aligning (enterprise wide) your corporate communications. It will seem like a very simple approach, and it is, but once you try to get consistent answers from the organization to the following questions (in order) you will understand why this is so challenging…and why so many companies fail.
Keep this in mind, effective communication to customers must happen through a consistent delivery of the right message, to the right customer, at the right time, in the right channels to facilitate effective, efficient dialogue.
This is how you do it. You have to be able to collectively (with the right internal groups) answer the following five questions in order:
- Who? – what audience/segment are you targeting, and why
- What? – what do you want/have to say to that segment that is relevant
- Why? – why would they listen
- When? – when do you contact them, and how often
- Where? – where do they want to receive the message
Sounds simple right? Here are a list of challenges you will face when go through the process:
- Who – right off the bat, you will find folks arguing about your target audience, the segmentation approach, the segments, etc.
- What – oh, you’ll have plenty of things you what to tell whatever audience you settle on but you will struggle with relevancy
- Why – now comes the killer question…why would they listen? Seen this question bring grown men (and women) to their knees. The reasons are many; Marketers don’t understand the products, products aren’t differentiated, etc. Getting this question right is the key to the whole process.
- When – the challenge is deciding on at what point in a sales process, a marketing campaign, events, etc., and the frequency of contact. Touch them too often and/or at the wrong point you’ll get opt-outs, too infrequently, you’ll get no mindshare.
- Where – notice that I said, “they”, and not “you” on where the communication happens. Yes, it’s about your customer and where they go for information not where you want to put it. Find out where your audience goes to get information and/or determine their perference for receiving it. The othe challenge is ensuring that the message fits the channel. Certain messages/value proposition, etc. fit a certain channel better than others. It’s worth the time to figure this out.
This approach creates an execellent output but it will take time, discipline and many iterations to get right…good luck.
by scott.gillum | Jul 19, 2012 | 2009, Marketing
My inbox is full of resumes of good marketers that I’ve been fortunate to come to know or work with over the years. Solid people, with great experience who are now having a challenging time finding new opportunities in this incredibly difficult economic environment. Many of these people could have had their pick of jobs as recently as last year. Given the situation, I thought I’d try to help by providing a viewpoint on what skills set, background and experience companies will be seeking once they start hiring again. I’ll use two data sources to make the case.
A few years ago, we teamed up with a professor (
John Josephs)at
Kellogg on a couple of research projects aimed at getting a better understand of what creates a high performance marketing organizations. Internally, we thought of it as the “head” and “body” studies because we first studied the marketing organization (
the body) and then the follow year CMO’s (
the head).
We surveyed not only CMO’s and marketers, but also CEO’s, about their views on what makes marketing effective. The research was then published by the
CMO Council. Here are a few things we discovered along the way.
CEO’s view on how to measure marketings performance
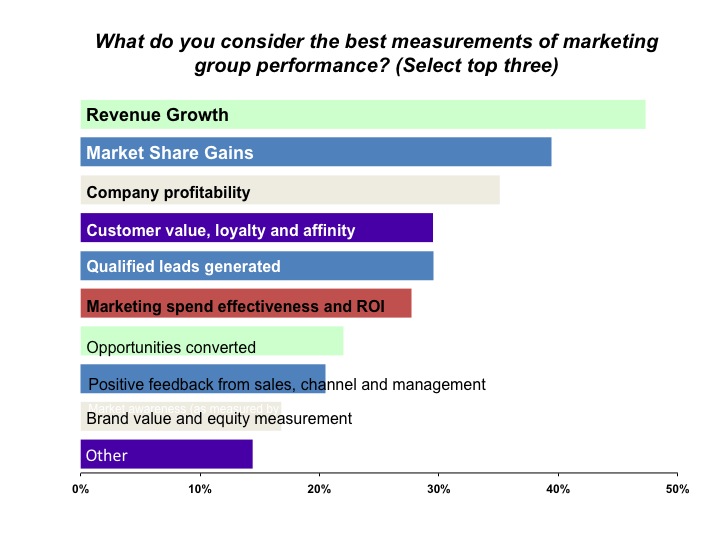
How CEO View Marketing Value and Performance
This information is a few years old now, but I can tell you that based on client work that the down turn has done nothing to change this, if anything, it has placed greater importance on the top 3-4 responses. Keep the top responses on these charts in mind as we move to the next section.
Last month, I was given access to a database of senior level marketers (SVP and up) to do some analysis for the organization that owns it. We looked at the background and experience of over 800 marketers with the following titles:
- 50% were CMO’s
- 32% EVP’s of Marketing
- 8% SVP’s of Marketing
- And interestingly enough 10% had CEO titles but had recently been the head of marketing
They came from large, medium and small companies including start ups:
- 25% – Large (over $500M)
- 32% – Medium ($100-$500M)
- 23% – Small ($50-$100M)
- 22% – Start up or under $50K
We were interested in assessing their area of expertise, experience and tenure.
Although executives with Product Management and Sales Enablement/Demand Gen experience represent only 27% of the total group, they represented a disproportionate amount of executives with the longest tenure. In fact, they were twice as likely (as a representative percentage) to be in the 2-5 years tenure category than those with Brand, Advertising and Corp Comm backgrounds. And they made up half of the individuals in the more than 5 year category.
Another interesting thing we picked up is that markerters in the NYC area were more likely to be new in role versus other regions (higher than average churn…probably attributed to a higher supply of talent).
Spencer Stuart has for many years reported CMO tenure rates (less than the life of a gold fish) but I’ve never seen them look at tenure by background…which makes a difference based on our assessment.
Finally, let’s look at Supply & Demand.
The Top 20 Advertisers in the US have been decimated. Think about…half of the Top 10 advertisers in 2007 were automobile manufactures. As a result, agencies have put hordes of people on the street.GDP in Q4 2008 is estimated to have declined by 6.2% from Q3 that declined by 0.5%. Revenues are down on average of 30-40% from the prior year in most firms (at least the ones we work with).
As a result, there are a slew of marketers with advertising, branding, and corporate comm backgrounds (73% of the database that we analyzed) in the market.
Let’s put it all together:
- CEO’s measure marketing effectiveness by revenue growth and market share
- CMO’s see the greatest need for new talent being driven by the integration of sales & marketing
- A large supply of “above the line” marketers exist in the marketplace
Conclusion– potentially high demand and a low supply of marketers who can drive revenue. The marketers that will be in the highest demand coming out of the recession will be the ones who have been aligned or have had direct responsibility for growing revenue. Marketers that can speak the language of sales. Unfortunately, it will be a slow process for folks with a Brand PR and Corp Comm or the Ex-Agency/Media guys.Marketers with backgrounds in Product Management/Marketing who have owned a P&L, folks with sales backgrounds and/or marketers who can show that they can drive revenue/growth will be in demand first.
The challenge for the other groups is that of supply. It’s not to say that good Brand and Agency folks won’t find positions it’s that it’s going to be hard. Expect that you will be competiting with many other qualified candidates and it may be difficult to differentiate yourself.
by scott.gillum | Jul 19, 2012 | 2011, Marketing
Original post date January 27, 2011
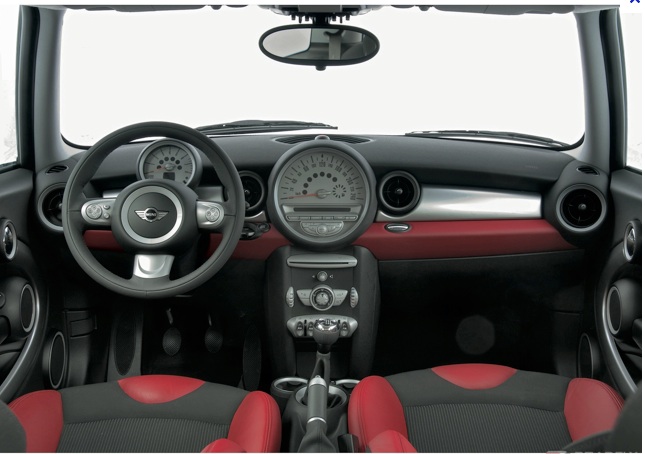
Owners of the MINI-Cooper have long been known to be one of the most fanatical and loyal of all call owners. They are likely to custom design their cars online, actively participate in local motoring clubs, and are in general, a passionate and faithful community.
A new project took me to the mid-west and I finally got a taste of the MINI-Cooper, courtesy of Budget rental cars. Initially, I was excited by the opportunity to find out what the buzz was about, but after getting in the little red car with white racing stripes, I quickly found myself totally discombobulated. It was like the car was designed by aliens, nothing was where it is should of been, and the layout, among other things still remain a mystery to me.
I couldn’t operate the windows the first half of the day, drove around with my blinker on for the other half. The radio settings were in the speedometer, and the tachometer was where the speedometer should have been. Even the gas gauge wasn’t a gauge at all, but rather a circle of lights.
The “Coop” had all the same instruments any other car has, but they were in different locations and/or in different forms. I’m still not convinced if the lay out of the dashboard is better, but one thing is true — I was fully engaged, I had to be. Even though I’ve been driving for almost 30 years I was a stranger in a strange land. Suddenly, driving was fun again.
It got me thinking about how we engage customers. There is a bunch of noise being made about customer engagement; the question for most of us is how to make it happen. Intuitively it makes sense, but from an execution standpoint, it’s still a bit of a mystery.
We have seen traditional response rates drop, and have begun experimenting with Social Media with little, to no, payoff. Although the true upside of customer engagement may still yet to be defined, a
Gallup research report points to it as a leading indicator for customer attrition. In some ways we’re searching for the Holy Grail, but maybe new isn’t the answer, maybe we have what we need.
As I sat at a stoplight and stared at the dashboard trying to make sense out of it, it hit me: It was if the MINI engineers intentional redesigned and/or rethought everything, most likely with the intent of keeping the Coop customer base happy and engaged with it’s quirkiness.
It showed me that you could create an engaging experience by leveraging what you already have. Granted, had I been on a tight schedule, I may not of enjoyed having to “get up to speed.” I was in a city that I had never visited and driving to see a client I’ve never met. I had my hands full directing the GPS, a stick shift, and a conference call.
I am not suggesting rearranging mission critical assets for key customers but what I am offering is this…maybe we need to rethink how customers engage and interact with our sales people, customer service reps, and the web. Like the engineers at MINI, we need apply our creative thinking skills to reordering our assets to provide customers with what they want, but delivered in new and intriguing ways.
At the end of the day the MINI still provides basic transportation – I got from point A to point B, but getting there was uncomfortable, scary, exciting and fun. Much of what we provide customers is basic “transportation,” and “mixing it up” can be scary, but it also may be the key to getting customers’ attention again.











