by scott.gillum | Jul 1, 2014 | 2014, Marketing
I just spent a week in the Caribbean on an island with lovely beaches and an incredibly high cost of living. The island has no income tax, so generates the majority of its income from tourist like you, and I, through a very large VAT tax.
Simple staples, like bread, are priced so high it made me ask my wife “How does anyone afford to live here?” The answer became apparent as the week went on — you’re either very wealthy (not us), or that you live very simply.
As the week progressed, I found myself appreciating the fact that less could be more. Once my awareness was raised, I discovered a certain elegance in the simplicity. For example, the cabinets and crown molding in our room were white washed rather than covered with layers of expensive paint, actually highlighted the natural beauty of the wood grains.
 Arriving home to the states and the “routine” with my newfound appreciation for minimalist living, I found that I am now highly sensitized to the waste within marketing. The unnecessary use of “empty” words used to make extravagant and/or over inflated claims that is cluttering copy.
Arriving home to the states and the “routine” with my newfound appreciation for minimalist living, I found that I am now highly sensitized to the waste within marketing. The unnecessary use of “empty” words used to make extravagant and/or over inflated claims that is cluttering copy.
It appears that with the proliferation of content marketing we are starting to see an ugly underside. Marketers focused on getting “views” and social shares, are in a “war of words” that is producing empty promises in the form of audience grabbing headlines that fail to pay off with insightful or promised content.
Words like “epic” or “iconic” once rarely used, (and when they were, they were actually describing something that was of a significant historical event) are now used to describe everything from trade shows to webcasts, so overused, they have become meaningless.
In the past, when someone made the statement that they were the “Leader in”, they actually were, and could back it up. Or when they created a “Top 5 List or Best Practices”…they had the research to actually prove it. Now marketers randomly use those enticing titles in headlines in a desperate attempt to get noticed.
Fueling this are insights from content marketing tools are enabling marketers to engage in this “copy cat” hype game. Just pick a topic, go to a site like BuzzSomo, search for the most popular headlines, and then build something similar.
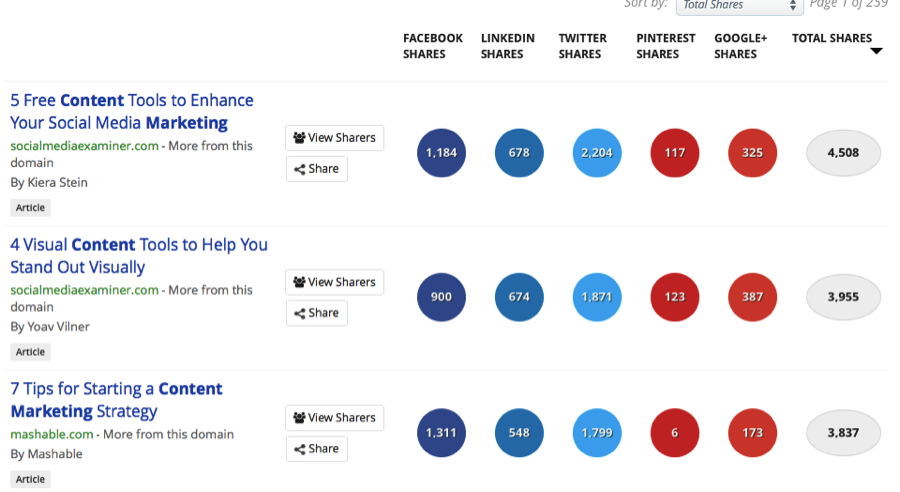
Content marketing, and for that matter Native Advertising, can benefit audiences and be effective marketing tools, but not if these practices continue.
Thanks to Steve Jobs and Apple, simplicity and “clean lines” are now pervasive within design. It has helped to streamline and simplify brands, from logos and website to products. The time has come for it to influence copywriting and content production.
Yes, it takes longer to write a shorter sentence, but it’s worth it. As the late great Maya Angelou once said, “Easy reading is damn hard writing. But if it’s right, it’s easy. It’s the other way round too. If it’s slovenly written then it’s hard to read.” As marketers, we have to do better, be better. Strive for elegance in your craft. Don’t paint the essence of what you want to say, or promote, with layers of needless or empty words.
If you want someone to read your content — be credible. If you want it shared, say something insightful or newsworthy. That is the way it has been, and will always be. It’s that simple.
by scott.gillum | Jun 23, 2014 | 2014, Marketing
I found this in a file earlier this week. It was part of a pre-work exercise for a well known professional services firm. We were engaged to help them redefine their corporate value proposition and messaging architecture. I thought it might be useful for the group.
Who Uses It?
Everyone:
- Marketing Teams
- Salespeople
- Recruiters
- Investor Relations.
What You Should Not Do:
Most elevator pitches miss the mark because:
- They are too long–“We have an elevator pitch but it requires a building with 700 floors…”
- They are too technical
- They lead with bragging points or product features — “We are the leading provider with 54 offices in 29 countries.”
- They are ego-centric rather than customer-centric—An elevator pitch is a response to the question what do you (or what does your company) do? When a customer asks this they mean, “what do you do for me? “
How To Do It Right:
- Be customer-centric
- Be concise (30-60 seconds max)
- Be true and “ownable”
- Convey business outcomes, not bragging points or features.
- Show, don’t tell— provide a story that will show a customer what your company will do for them.
Best Practices:
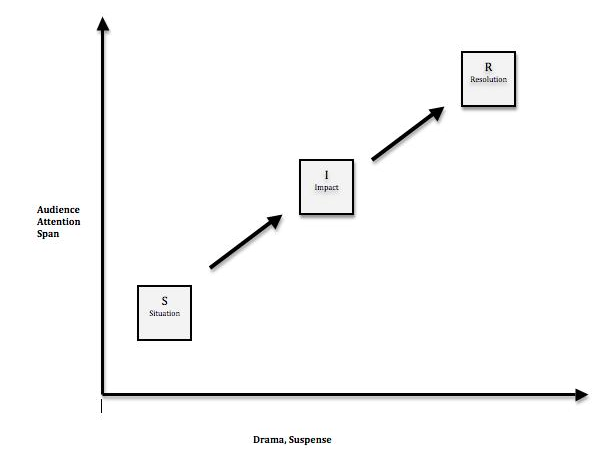
Elevator Pitch Should ‘Tell a Story’ that:
- Addresses: Situation, Impact and Resolution
- Starts with customers; ends with outcomes
- Quantifies your value proposition
Try beginning with a provocative statistic
It should consist of three parts:
- Situation – cite the dilemma, pain, difficulties or complications that the prospect faces…
- Impact – quantify the impact that the situation is having on the prospect’s bottom line…
- Resolution (Solution) – how do you solve the problem?
by scott.gillum | Jun 10, 2014 | 2014, Marketing
Tell me if you have heard this before; “we need more, and/or better leads.” The chances are, if you’re in hi-tech marketing you may hear it on daily, weekly and monthly basis. Why? According to Forrester consultant Tom Grant, it’s because of the need to feed the funnel.
In his report Tech Marketers Pursue Antiquated Marketing Strategies Grant compared hi-tech firms to other industries “B2B technology companies treat marketing as an opportunity to sell new products and services to new customers.” As he stated “the product is the axis around which marketing efforts turn,” and as a result, the primary objective of marketing is to produce leads.
Similarly, marketers have long held the belief that because of sales short-term focus on making quarterly objectives, it either lacks the appreciation of, and/or the sophistication to understand anything other than lead gen, for example longer-term brand building and awareness activities.
But what if both of these viewpoints were actually wrong. What would happen if you asked sales what they valued, rather than assumed you knew the answer? How might it change how marketing thinks about its impact on the organization?
For one B2B Tech Company, feedback from the sales force is helping them refine their value to the organization. “When it comes to enabling the sales force, we’ve previously relied on what I call “measurement-by-anecdote.” Our goal with this study was to quantify what sales values from marketing so we can focus on the things that make a difference.” said Rick Dodd, SVP Marketing of Ciena, a $2 billion global optical and packet networking company.
To gain that insight the company surveyed its global sales force, including five types of sales reps covering five different account types. Over 400 sales reps provided feedback on their priorities for marketing and marketing’s performance.
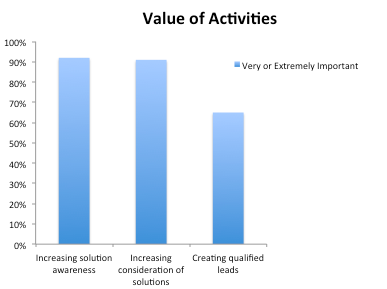
According to sales, the highest ranked marketing activities were at the top of the funnel, 92% of sales said that increasing the awareness of solutions was very or extremely important, increasing consideration was close behind at 91%, only 65% mentioned lead generation.
“Our sales force is very experienced; they understand that technology and industries change quickly. We’ve obviously been successful positioning ourselves for today’s market, and now we want to take best advantage of the big shifts in our landscape. The survey showed us that for sales to be successful, marketing has to be able to change customers and prospect perceptions,” according to Dodd.
Perhaps the most interesting insight to come out of the research, is how Ciena is now thinking about measuring and reporting marketing’s impact on the organization. “Measuring pipeline value is a struggle in our business”, said Bill Rozier, VP of Marketing. “We have long, complex sales cycles that make it difficult to isolate marketing’s impact.”And they are not alone it in that challenge. The Aberdeen Group’s recent Demand Generation study found that 77% of respondents rated visibility into lead performance across stages as very valuable, but only 43% indicated they can do thi effectively.
Instead of spending a lot of time and energy in trying to perfect an imperfect process, thecompany is focusing efforts on measuring marketing performance at the macro level. “At the end of the day, our performance is ultimately measured in sales success, so that’s what we are focusing on measuring”, said Rozier.
To do that, the company has created a quarterly dashboard from the survey. Two regional sales organizations each quarter will be asked to evaluate marketing’s performance in three areas: 1) Marketing’s contribution to sales success; 2) Marketing’s performance compared to competitors; and 3) Marketing’s contribution to the success of the organization.
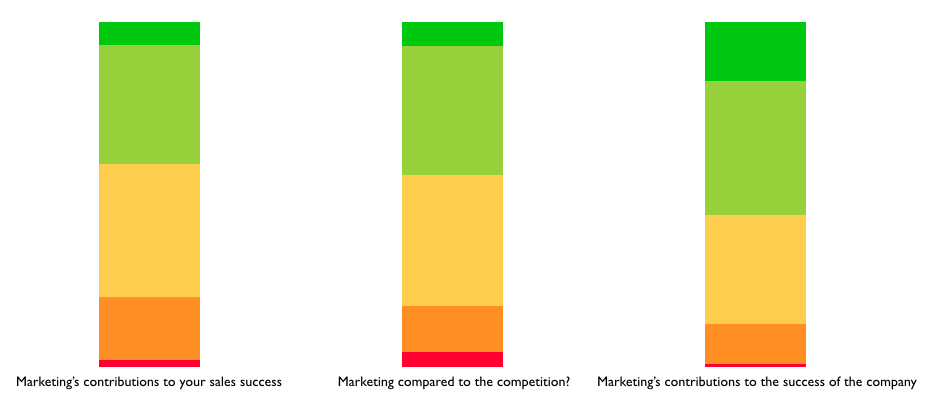
It’s a unique approach, and perhaps one that should be considered by others, because the challenge in performance management is often in defining the right metrics to drive the intended behaviors.
Ciena’s approach, as Dodd concludes, is to put the focus on the right conversation; “As we learned through the research, contributing to the success of the sales force isn’t just about one thing, it isn’t just lead gen. I appreciate that they give us credit for doing a good job when compared to competitors, but what we’re most interested in understanding is how well are we doing in enabling them to win. If the sales team rates our contributions as being valuable to their personal success, then we know we’re doing the right things.”
by scott.gillum | Apr 11, 2014 | 2014, Marketing
Take out a piece of paper, and write down what you think makes your company different from its competitors. Now, Google your competitors and see if you can tell the difference between what you wrote, and how they describe themselves. If it sounds the same, keep reading.
Let’s say you’re the CEO of a fortune 500 company looking for some advice. Two top tier global consulting firms are recommended, and based on their website descriptions of “Who They Are” which one would you chose?

Can’t decide? That’s the challenge I’m talking about. Although one firm uses “advisors”, they are describing what the firms do, not who they are, and as you can see, the sound the same. If some of the smartest guys in the business are getting it wrong, and they’re the “advisors to the world’s leading businesses” you shouldn’t feel bad.
Why is it so hard? There are two key reasons; the first being in B2B, we are conditioned to think that what we do is who we are. It’s the Achilles heel of effective marketing communications, the bad habit of over communicating and focusing what you sell (what you do) versus who you are (what makes you different).
Making things worse is when B2B marketers talk about the value of what their company does, they use terms associated with business value, the functional benefit or business outcome of the product or service being sold (e.g. increase revenue, reduce cost, retain customers, etc.). It’s non-differentiating because competitors use the same language, and that’s the second major challenge to overcome.
Over the years, marketing communication has evolved from talking about how great the company was to talking about what it does for customers. Thankfully the “we’re number 1” days are over but unfortunately, the “what we do for customers” has been defined by what the company sells. It is time to evolve again and speak to more about the “DNA” of the organization. Research from CEB has shown that buyers figure out what companies sell (what you do) relatively quickly. It takes them much longer to figure out why they should buy from one company or another.
And surprisingly, when they do make the decision, it often has little to do with “business value” of the product or service itself, and more to do with the emotional connection they feel to it, or to your brand. Buyers are not the rational beings we once thought, they do business with businesses for very personal reason, according to the CEB research. As a result, they want to get to know the company as well as they know the product or service.
So, how do you “humanize” the company? Here are some tips to get your started:
- Ask customers – sounds obvious, but rarely happens. Ask them why they do business with your organization and others. You might be surprised by what you’ll learn; it may have nothing to do with your products or services. Use this information to communicate back to them “who you are” in the language and context that is meaningful to them.
- Survey employees – this may help uncover why the organization can’t get on the same page when it comes to defining the company. Employees have a tendency to define the company and what it does, based on their own experience with the products they know, and customers they serve. As a result, they have a myopic view of the organization. You will find multiple views on your value, and the type of company you are, across your organization.
- Decide on the type of company you are – pick up a copy of Michael Treacy’s Discipline of Market Leaders. In it, Treacy and Fred Wiersema define three value proposition types based on business models; Operational Excellence, Product Leadership, and Customer Intimacy. Use this framework as a starting point to define your organization and its’ language. It also helps get everyone on the same page.

- Create a persona – once you have consensus on the type of organization and its value to customers, it is time to figure how to differentiate it. In this step, use brand archetypes to help define the company persona. Here’s a free list of 40 archetypes. Create a working session and have the group discuss how the company views the world, how it reacts to bad or good news, how it speaks — what is the tone? Keep the conversation away from what the company makes or does, and on the organization itself.
Buyers have changed. They want to know who you are, because they already know what you do. And they’re looking for a little of themselves in your brand. Relate to them on a human level. Tell them who you are in a way that connects with them. If you do, it will differentiated you, because like people, no two organizations are exactly alike.
by scott.gillum | Jan 28, 2014 | 2014, Marketing
In December, I had the opportunity to be the Keynote speaker at the Bowery Capital CMO Summit in NYC. The event featured a number of high profile CMO’s speaking with an audience of mostly early stage startups (under 20 employees).
My presentation was based on the recent Forbes blog post Everything We Thought We Knew about B-to-B Marketing in Wrong. The audience also included some local media, a reporter from CMO.com wrote a summary of the speech.
http://vimeo.com/82457497
by scott.gillum | Dec 2, 2013 | 2013, Marketing
My initiation into the world of sales happened at the height of the “Glen Garry Glen Ross” days. It was the time of “blue suits” and “fast talkers”, and not a piece of sales automation or tracking technology anywhere to be found.
We’d roam our territories searching for conversations hoping it would lead to something more. At the end of the day, we’d return to the office and put our “numbers” up on the board; # of conversations, # of leads, and closed deals ($). The white board was our “sales dashboard” highlighting performance against goals for the month, and year-to-date. Our view, and control over our success, was determined day-to-day.
Over the last 25 years, sales has been enabled with a broad set of new technologies, from sales force automation to CRM to cloud based mobile sales tools. All aimed at helping the sales organization better track, measure, and achieve quota. And with each advancement in technology, sales has gained the feeling that it has more control over the process, and outcome.
The buyer’s journey is marketing’s “shiny new penny”. Over the last couple of years, numerous consulting firms have produced research trying to map the journey with varying estimates on how late in the journey customers are now engaging sales.
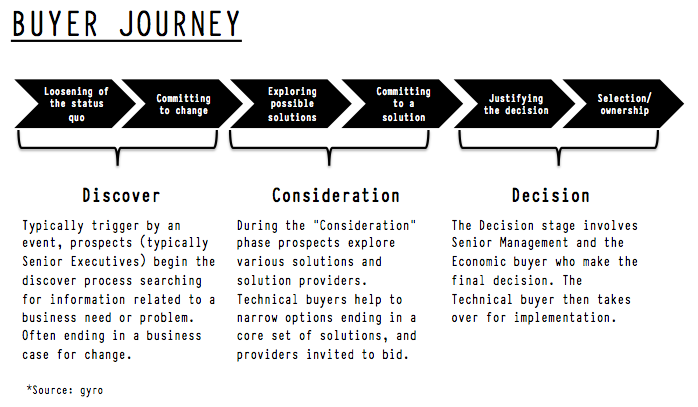
Before you go off preaching this newfound perspective on how buyers are now in control to a sales organization, who might just have a counter viewpoint, there are some things you need to know:
- This is not necessarily “new” news – educated buyers have been engaging late in the process for years, and in some cases, bypassing the sales reps all together ordering direct. What’s different now is that we have better tools to track their behavior.
- It can be threatening – sales folks “cover” buyers, be it a prospect or an existing customers. Their job is to start a conversation and to continue the discussions to, hopefully, a successful outcome. They can’t be everywhere, or everything to everyone, but to suggest that they are not providing buyers with the right information at the right time, or that they may not be “covering” them will cause a defensive or hostel reaction. Be tactful in the way you present the findings.
- Buyers channel surf – don’t assume that buyers are only online in the early stages of the buyers journey, and likewise, that they are only talking with sales in the late stages of the process. Unlike the past, when we could estimate where customers were in the sales process by watching how they engaged with content and channels, buyers now use all channels, and all information sources, at all stages of the journey.
- Good sales people already get it – good sales people are very intuitive by nature. They already have a feel for how buyers research and purchase products. They also know how to use the best content and/or tools to help buyers advance their learning and to move the process. As a result, they will want to know how you can help them.
- Have a Plan – especially for the sales people I just mentioned. The question that you should expect to get after sharing the information is; “So what now? Given this new insight how should we change our sales and marketing approach.” Make sure you have an answer.
My gut reaction was that the buyer’s journey would pose a significant change for sales, I now realize that it’s a much bigger challenge for marketing. Given the amount of time spend online in the research phase, buyers already have a good feel for the “business value” of your product or service by the time they engage sales. It’s why they have put your organization in the “consideration set.”
The challenge, according to recent research, is that buyers are unable to differentiate your product or service from the 3-5 other companies they are also considering. To create separation, you must be able to illustrate and communication “personal value”.
And that has not been a strength of marketing, but it’s a core competency of good sales people. Use this opportunity to partner with sales to developed content that resonates with buyers on emotion level deeper into their journey. Sales may be losing control over the buying process, but they know how to connect on a personal level with individual making the purchase decision, use that to your advantage.
 Arriving home to the states and the “routine” with my newfound appreciation for minimalist living, I found that I am now highly sensitized to the waste within marketing. The unnecessary use of “empty” words used to make extravagant and/or over inflated claims that is cluttering copy.
Arriving home to the states and the “routine” with my newfound appreciation for minimalist living, I found that I am now highly sensitized to the waste within marketing. The unnecessary use of “empty” words used to make extravagant and/or over inflated claims that is cluttering copy.












