by scott.gillum | Jan 28, 2014 | 2014, Marketing
In December, I had the opportunity to be the Keynote speaker at the Bowery Capital CMO Summit in NYC. The event featured a number of high profile CMO’s speaking with an audience of mostly early stage startups (under 20 employees).
My presentation was based on the recent Forbes blog post Everything We Thought We Knew about B-to-B Marketing in Wrong. The audience also included some local media, a reporter from CMO.com wrote a summary of the speech.
http://vimeo.com/82457497
by scott.gillum | Sep 22, 2013 | 2013, Marketing
Do you think the senior executive team is excited about the big lead generation campaign you just launched? Nope. How about the number of “Likes” on your corporate Facebook page? Think again. Marketing doesn’t matter in many organizations, because it thinks, operates, and worst of all, reports “small.”
Executives sitting in the “C-suite” got there by thinking big, managing big, and reporting “big”. Marketers commit hari-kari with this group by reporting tactical level activities – “minutia,” that garners no ones attention. Do you think the head of sales is reporting the number of sales calls reps make a day? No. If you want to get their attention, you have to make marketing more important to them. Here are five ways to go “Big.”
- Big Bets – if you want marketing to be valued you have to understand, and link, to what the organization values. It’s that simple. If it’s market share, connect marketing objectives and activities to acquisition or/and account penetration. If it’s profit, understand the drivers and align your teams’ efforts appropriately.
- Big Strategy – once you understand how to link marketing to the business objectives your job is then to connect those big bets to day-to-day marketing activities. Your smarts will be needed to take the marketing requirements from the product and sales organizations (which may be very tactical) and link them to the overall marketing strategy that aligns to the “big bets.” Warning – this will require math, perhaps lots of it.
- Big Plays – to execute, organize your marketing objectives as defined by your internal stakeholders into 2 or 3 “big plays.” If market share is a key growth objective, a big play should focus on an area that has the greatest opportunity to do that…a specific market, product and customer. All marketing activities/campaigns should be nested around that “play.’ Messaging is critical here because it is the “big play” wrapper that creates consistency in the communication across execution –think “Smarter Planet.” IBM discovered years ago that the best performing campaigns stayed in market the longest, and had the highest level of integrated tactics. It takes focus and discipline to do, but if you can get there it will make your life easier by allowing you to organize everything under a big play umbrella, and if things don’t fit…then maybe you don’t do it.
- Big Results – the first rule here is to understand that measurement and reporting are different. Measure everything, but only report “process” or “results” metrics. Executives care about “outputs,” not “inputs.” Inputs are activities, outputs are results, know the difference.
- Big Balls – ya gotta have ‘em. You are going to have to get comfortable with, and embrace risk. If you do this right, you will be placing bets, that at the time, you will not know how, or if, they are going to pay off. Years ago, I worked with a CEO that committed to double the size of the business in three years. The CMO calculating sales cycles realized to support that growth marketing needed to double the number of leads that year. She had no idea how she was going to do it, but it caught the attention of the senior management team, focused her team, and it happened. But as she learned, you don’t try to go it alone. Reach out to others with your plan, get their buy-in and support. Level set expectations on timing and performance, it may require a significant investment in time and money for the “big bets” to pay off. Set big goals, but be realistic in getting there.
The time for going “big” is now. In Forrester’s recent B2B CMO’s Must Evolve or Move On report, 97% of marketing leaders who were survey agree with the statement that “Marketing must do things that is has never do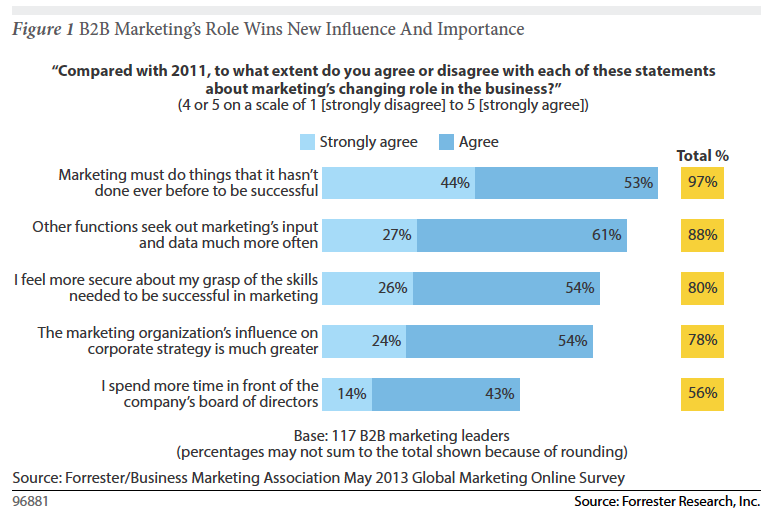 ne before to be successful.”
ne before to be successful.”
The other interesting, and important nugget from the research is that marketing is playing a bigger role in influencing corporate strategy, and other functions. Make sure you’re capturing this opportunity at your organization by thinking, and by being — “Big”.
by scott.gillum | Sep 27, 2012 | 2011, Marketing
Original posted on Forbes July 25, 2011
Years ago some colleagues of mine built what we thought at the time was the “holy grail” of business marketing: A sophisticated analytical tool that could tell a marketer where to invest, why, and what the return would be in sales productivity. It could also tell them where to cut dollars, why and what the impact would be on the business.
It was an incredible feat of analytical modeling and technology. Built for one of the most respected and well known companies in the world, so the CMO could answer with absolute certainty the CEO’s question: “What am I getting for my marketing spend?” We thought that it was our ticket to the big time and the rocket to ride to explosive growth, but that was not the case.
It turned out to be the only one we sold. And that always baffled me. Anyone who saw the tool was awed by its power and insight, but they didn’t buy.
Over the years, I picked up some clues as to why others would not buy:
- The head of a major west coast based IT company warned us that our business intelligence tool and analytic model might limit his managers’ ability to make decisions based on their experience … “gut feel.”
- The CMO of a global software company was concerned that our meticulously designed marketing processes, with stage gates and Gantt charts might limit his team’s creativity.
- The head of marketing finance at a major Financial Service company told me that every year they run their marketing optimization model and it tells them that they overspend on TV, and under spend in print. But at the end of the year if there was additional budget leftover the CMO puts it in TV.
I’ve now been able to put the pieces together. I came from a marketing science world and have since learned to appreciate and understand the value of the art of marketing.
Data and analytics can tell you where customers are, what they look like, what they’re interested in, but science alone can’t make customers buy. It can’t make customers advocate for a brand, and it can’t make the hair stand up on the back of their necks.
Insightful, creative and relevant ideas that trigger human emotions can – and do – sell. For as much as I wanted to believe that buyers were rational creatures behaving in predictable patterns, I now understand that they are not.
Marketing, as much as we want it to be, is not an exact science. Technology innovation has allowed us to better understand buyers, influencers and the performance of our activities.
But at the end of the day, business is personal. We can’t remove the human element from the buyer or seller side. Relationships and perceptions matter, how a product and/or a brand makes a customer feel is important, and it’s not easy to model or predict.
And with that, I found the answer: Although helpful and informative, good marketers don’t need to rely on sophisticated analytical tools to make decisions. Their experience, “gut,” and sometimes the hairs on their back of their neck do just fine.
by scott.gillum | Sep 21, 2012 | 2011, Marketing
This post was originally posted on July 8, 2011. It also appeared on Forbes.com
Here’s a hypothesis: Given the greater focus on ROI, marketing automation tools, and enhanced tracking of results, marketing is more of a science than ever. Therefore, marketers’ ability to defend and validate their value among peers should be easier than ever before.
So why does a recent study by Fournaise show that CMOs still lack credibility with CEOs?
The study points to several deficiencies with an emphasis on communication – are you sensing the irony? Further, marketers tend to sabotage themselves in everyday interactions with the larger executive team, and in many cases, have no idea they are doing it.
Here are five common mistakes among marketers:
- Stumble explaining the value of marketing. Asked almost daily, and rarely answered properly. The key is to understand how the inquirer perceives the role of marketing. The question behind the question is “what is the value of marketing … to me?” According to the study, it most often relates to “revenue, sales, EBITA or even market valuation.”
- Limited product, service, and customer knowledge. Even the savviest marketer will arrive DOA in the credibility department if they fall short on this one. And it is not about feature or functionality, but rather customer use and application that matter most and those factors vary by industry and size. Leave “speeds and feeds” to the product organization. Marketing’s job is to differentiate and develop compelling value propositions that sell. If products are built “inside-out,” then bring the “outside-in” perspective.
- Can’t Dance. Marketing comes with highly visible risk and things are going to go wrong. When they do, marketing needs to learn how to dance. Handling these situations will define how marketing is viewed. Keep best and worse case scenarios in mind when briefing the executive team. Truth is, if marketing isn’t making a few strategic and tactical mistakes, it’s not moving fast enough. As a former IBM client told me, “If you fail, and you will, fail fast.”
- Isolation. A favorite question from sales: What have you done for me lately? And the product team can be equally demanding. However, marketing has to build, nurture, and maintain strong relationships with these groups. For Sales, it is helpful to establish an integrated sales pipeline and hold weekly pipeline meetings; this will build rapport and create a common sense of purpose. It’s also an opportunity to put marketing metrics in a sales context. The key to a successful relationship with sales is about communication and performance. For the product group, marketing needs to clearly define points of integration for research, content, and value proposition development. The key to a successful relationship with the product team is about process and integration.
- Where to invest – or cut – an incremental dollar. This question is posed by the CFO at the end of the quarter when numbers are off, and by the CEO who wants to redirect budget. It’s also used as a test. As a holder of discretionary dollars, marketing has to be prepared to answer “where” and “why” along with stating the business impact. In talking about CMOs, 72% of CEOs say, “[marketers] are always asking for more money, but can rarely explain how much incremental business this money will generate.”
To call out the sense of irony, most of these issues are communication related. The same rigor brought to external communication needs to be applied internally:
- Know the audience
- Understand their needs
- Communicate to them in their language.
While the Fournaise study states that executives think in terms of “revenue, sales, and EBITA,” most make judgments based on their emotions. Marketers are advised to use their creativity in delivering the message.
Friedrich Nietzsche said it: “All credibility, all good conscience, all evidence of truth come only from the senses.”
by scott.gillum | Aug 10, 2012 | 2012, Marketing
In 2004, I was part of research project with a professor at the Kellogg School of Management and the CMO Council that sought to understand what CMO’s believed to be critical for their success. The most common response was a seat at the table with other senior executives.
Four years ago, I was part of another research effort focused on the CMO’s top priorities, and number one on the list was to be viewed by their peers as strategic thinkers. Finally, I believe the day has come for that to happen.
Marty Homlish, the CMO of HP believes the line between business and consumer marketing is disappearing. Homlish states, “ Behind every B-to-B company is a consumer. The way you communicate to that person is as an informed consumer.”
Technology has allowed work to follow us home and our home life to the office. It has blurred the line between our personal and business personas. The concept of being ‘at work’ is now more a state of mind rather than a physical location or particular time of day.
If business buyers – who were once thought of only as rational decision makers – now need to be communicated with as informed and emotional consumers who no longer fit our past perception of work hours and locations, what might this mean for the future of business-to-business marketing?
To answer that question, one must first understand the difference between how business and consumer marketing operate. According to a Booz & Co and the ANA in The New B2B Marketing Imperative study, B2B marketing has primarily taken an “inside out” approach, focused on the needs of the company and accounts rather than customers.
By contrast, 85% of B2C marketers, who take an “outside in” approach said they were involved in growth initiative decisions which are considered to be strategic such as new market entry, customer relationships and market driven product development.
Additionally, 42% of B2C marketers play a key role in building customer relationships, versus 8% of business marketers. B2B marketers said that “Customers are rarely driving the process and their input is seldom integrated from end to end.”
If today’s business buyers really are “educated consumers” as Homlish suggests, then business marketers can no longer be left out of customer and product conversations. It also means that organizations that target business buyers, who has given lip service to transitioning from being “product led” (inside out) to “customer focused” (outside in) now need to act. And the tip of the spear for driving that change – is marketing.
By better understanding and influencing the needs, desires and emotional drivers of individual business consumers, marketers will be in the strategic conversation and lead the transition. This is the key to unlocking the executive suite.
However, the organization is not just going to give marketers a seat at the table and there is a good possibility that executives don’t get it. As one of the marketing directors said in the study; “Marketing is just not in the DNA of senior management.” You will have to make it happen.
The study concludes that; “Core marketing capabilities – those that directly influence customers – have the highest correlation to market share growth.” Senior executives may not understand marketing but they do understand growth.







