by scott.gillum | Jul 20, 2017 | 2017, Observations
 There is a grocery store a few miles from my house. It’s small and older, at least thirty years in its current location. Usually, the shelves are poorly stocked with a limited selection compared to the newer stores surrounding it. Despite these facts, the store manages to stay in business which is somewhat hard to comprehend given the cut throat, low margin nature of the industry. It survives because it has a secret weapon.
There is a grocery store a few miles from my house. It’s small and older, at least thirty years in its current location. Usually, the shelves are poorly stocked with a limited selection compared to the newer stores surrounding it. Despite these facts, the store manages to stay in business which is somewhat hard to comprehend given the cut throat, low margin nature of the industry. It survives because it has a secret weapon.
His name is Andres. He’s a cashier and has been at the store for twenty plus years. Andres speaks five languages and knows most of the customers by name, typically, greeting them in their native language. He knows where everything is, or isn’t, and if it’s not there he knows when it will arrive. He is the store.
While some customers, like my wife, frequent the store because it’s convenient, and quick, as long as the item is on the shelve. The majority of the customers go because of Andres. The store is in an affluent international neighborhood with many retirees. These core customers have time to shop and chat with Andres. For them, a trip to the store is an experience, not an errand. I haven’t seen the numbers, but I would guess that the revenue per square foot is why it survives.
The interesting thing, having worked with B2B companies for the past twenty years, is that many of my past clients also have an “Andres.” His, or her name may be different, but their role inside their organizations are not unlike Andres. They know the customers, how to get things done, where the “dead bodies” are buried, and how to navigate the complexity of the organization. They are the company.
As organizations rapidly move to “digitalization” and look for AI to play a larger role in customer interactions, they need to consider the importance of these essential employees. Like the grocery store, there are customers who may be highly profitable that aren’t doing business with your company because it’s convenient or fast. They are and have been customers, because of the experience. And a good portion of that experience is shaped by the “Andres” of the organization.
As other grocery stores move quickly to eliminate cashiers, Andres’s store has no self-checkout or online store pickup. Management seems to recognize the importance of the shopping experience, which seems to make up for the lack of selection and inventory. As your organization moves toward the future, does the management team fully understand that not all customers are the same, or want the same things. They may also speak separate languages and while self-service may work well for some, others want the full experience, which may include a personal conversation with their “Andres.”
by scott.gillum | Feb 2, 2017 | 2017, Sales
The organization has a short-term ‘sales culture’ so almost everything marketing does is oriented to creating a lead. You know that there are larger system/infrastructure issues that are impacting performance but you can’t anyone to invest/focus on them. You’re on a trend mill running as fast as you can, but going nowhere.

It’s a nightmare thousand of marketers are living everyday, so let’s get to fixing this issue, permanently. The problem, at its core, is money. Yes, resources and time are also issue but the bigger challenge is that you have is a budget loaded with program dollars intended to be spent on media, events and other lead generating activities. Unfortunately, little are earmarked to fix the web infrastructure, navigation and content issues that are keeping leads from converting. You have a system problem, without system dollars to fix it.
Step one in the process is to get a capex budget. Just like the one used to build the corporate website. And get a big one, depending on size of the website you’ll need at least $500K, and perhaps over $1M, to build a “system” that will improve conversion rates. Here’s how you’re going to spend it.
- Assessing Search – does the organization know what it wants to be known for (what topics, products, solutions) and how audiences search for those items? If not, pull together a top 10 list and get to work finding out. Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Moz Open Site Explorer and Moz Keyword Explorer to gauge popularity and set priorities from your existing website.
- Increasing SEM spend – after assessing your top 10 priorities you’ll most likely find you need to increase your spend to improve your position. Determine how much, and for how long.
- Inventorying & Assessing Content – while your marketing dollars are working to help audience find you, the next step is to help visitors find the information they are looking for quickly. Assess the content on the following criteria: relevance (is it current, audience aligned, and insightful), accessibility (clicks and public view), and scanablity (ease of assessing key points)
- Evaluating Readability – time to take a hard look at the content you’re producing. Is it written in the audience language or your engineers? Is it compelling, will it engage audiences. Use tools like Flesch Kincaid Reading Ease and the Gunning Fog Index to help score content.
- Modifying Content – this could be painful. Try to leverage existing material. If you have videos, carve them up into 2 minute or less “snackable” insights. Long form content like white papers, etc., do the same. Chunk content into smaller more digestible bits. Next, create templates and guidelines for producers to follow so they know the type of content that will work best for marketing needs.
- Investing in UX – find out how visitors really navigate your site. You may be shocked by their lack of sophistication, and patience. Use tools like Validately to help assess users experience with your web properties.
- Optimization Everything – create pilot pages based on the UX findings and watch how visitors navigate and consume content. Use tools like Hot Jar to help track visitor clicks. Set performance metrics for bounce rates, time on page and conversion rates. Performance optimization is an ongoing effort so become comfortable with constant experimentation.
- Training Everyone – to produce the right content, invest the time and resources to train on how to use the new templates — product marketers on how to produce audience focused content, marketing folks on how to write ad copy that’s compelling, etc. Use insights gathered in steps 5 and 7 to convince folks to get onboard.
- Hiring an advisor – if this sounds like a lot of work, it is. If you don’t have the staff, the time, or the desire to take it on get someone to help you. You have a day job producing leads so put someone else on a parallel path of improving the process and performance. Chunk up the work plan mentioned above into quarters, align it to the marketing and the organizations priorities and set reasonable expectation on making progress.
Inbound marketing, content marketing, digital marketing, whatever you want to call it is not a marketing “tactic,” it is an ecosystem built from the outside in and requires a system thinking approach. The steps above will help you pinpoint issues within the system. “Digitalizing” an organization starts with audience facing sites so try to align this effort with any organizational effort related to digital transformation.
Getting the funding, use data points to prove the value of building a robust inbound lead generation capability. According to CEB, 71% of buyers start their purchase journey on the web. Build a market visibility index using your pipeline/waterfall metrics and market share. Reverse the numbers and find out what percent of the total opportunities available are in your pipeline. If you need more benchmarks, download Hubspot latest report on inbound marketing.
Need a case study? The process I just describe was implemented at a client this year. The results of the investment and effort have produced a 95% increased in MQL’s and an improvement in conversion rates by 65%. Inbound is now the top lead source in volume and performance. This organization has a hardcore outbound sales culture…which now, believes in the power of inbound marketing.
by scott.gillum | Sep 14, 2016 | 2016, Marketing
By Scott Gillum and Paige DiPrete
Modern marketers are “technology crazy,” constantly searching for the latest innovation to help them optimize the customer lifecycle and gain a completive advantage. For better or worse, marketers have plenty of options to play with, according to Scott Brinker the MarTech landscapes is enormous with 3,874 ISV’s and growing everyday.
In the past, Larry Ellison would of referred to the maturing MarTech space as a “killer field.” With the “Big 5” (Oracle, IBM, Salesforce.com, Adobe and SAP) swooping in like birds of prey picking off niche providers to fill out their product portfolio.
Marketers in the past would have been content with letting the industry leaders pick the winners and losers from this vast field of options. Preferring to consolidate their technology needs with one or two vendors making it easy to have “one throat to choke.” Companies like Oracle, have invested in making acquisition to fill solution gaps in functional areas as they have built their Marketing Cloud.
Unfortunately for Oracle and others, Millennia’s are not behaving the way traditional software buyers have in the past. In fact, there is growing evidence that they are pursuing a “best of bred” approach aimed at stitching together multiple platforms that follows the customer journey. Marketers are arranging their “stacks” either in a linked multi-platform approach, or with a spine in tag management products that hook up to an assortment of specific platforms and ISVs.
These new customer-centric clouds cut through traditional inefficiencies to motivate purchase intent. They are woven on the idea that consumers search for and choose customer-oriented brands, so marketing technology should reflect and enhance this in the evolving digital world. Most clouds only offer targeted suites in functional areas, which create both customer and internal silos. But these hybrid clouds humanize the digital experience and bridge integration seamlessly across all channels and touch points. All customer-facing departments are poised to address the public with a single strategy organized into one set of solutions.
A growing leader in the experience cloud space is Sprinklr, recently valued at $1.8 billion. Sprinklr has a focused acquisition strategy that concentrates on integration and is unlike any other in the business. First off, it doesn’t sweep up tools simply to increase their client base or rapidly grow, but it instead targets how well each can augment the customer’s experience. Sprinklr then completely rebuilds their software onto its own platform to ensure seamless integration.
And this could present a major challenge for the Big 5, as Oracle’s president Mark Hurd calls the idea of perfect integration between its products impossible, adding that, “There will never be a day where the depth of integration, unless it was all built from the bottom ground up, will be as integrated as any of us would like.”
When Sprinklr made its initial acquisition in 2014 of the Dachis Group, it was able to launch the first end-to-end operating system for brand marketing that enhanced customer relationships through multiple channels and touch points. Since then, its business ventures have made it a pioneer in converged media, advocacy, social communities, content management, audience segmentation, and social visualization – all to enrich its clients’ understanding of and engagement with customers.
Even though Sprinklr may be the fastest and most effective solution so far, it’s not alone in the move to deliver this new breed of experience clouds. In 2014, Gartner predicted that 89% of companies would be competing mostly based on customer experience by today, versus the 36% four years ago. The leading cloud giants like Oracle, IBM, Salesforce, and Adobe are starting to recognize this new wave and have shifted their strategies accordingly to offer their own experience clouds but integration remains a challenge.
Salesforce recently acquired Demandware as an integral part of its Customer Success Platform, but it yields weak integration between its various clouds. Similarly, Oracle and IBM are especially vocal about their experience cloud offerings and each present a large number of comprehensive solutions, but they are also limited on the integration front, both internally and with third party plug-ins.
It’s still debatable if there will eventually be “one cloud to real them all” but for now, the successful platforms will be those that can serve as a solid backbone through internal as well as external integration. Or as Sprinklr Founder, and CEO Ragy Thomas states it “Sprinkle, don’t shout. It’s not about who yells the loudest. It’s about who offers the most value in a relevant, nurturing way.”
by scott.gillum | Aug 12, 2016 | 2016, Marketing
This summer we gave our intern, Paige DiPerte, the herculean task of helping us make sense of the constantly expanding universe of MarTech. In this post, Paige gives us a glimpse into the world of interactive content, and identifies some providers to check out. 
It’s no secret that engaging content creates more value for users and extends their loyalty as customers, and the vanilla content of whitepapers, eBooks, or infographics is not cutting it.
Even though Buzzfeed quizzes tend to be kitschy, these methods of engagement consistently are listed as “Trending” on the site. From finding out which Harry Potter character died last to learning instructions for how to operate a device, users are choosing engaging content like assessments, calculators, polls, brackets, and interactive videos. It’s not a surprise that DemandGen shared in 2016 report that 84% of B2B buyers prefer interactive content, while 83% want content to be more interactive.
This rise of active and personal learning puts users in a place to engage with content and then make informed, substantive decisions. This powerful form of absorption is beginning to shape marketing consumption into a constructivist framework.
At the same time, behind-the-scenes, marketers are donning the white coats of realists. Careful observation and analysis of the data gleaned from interactive content is a marketer’s gold mine.
Traditionally, marketing can infer a user’s “digital body language” from a footprint of website history, clicks, downloads, and emails opened to generate lead scores and segment labels. Problems, however, arise both in communicating intent through the data and in the traffic between marketing automation platforms (MAPs) and CRM tools.
The emergence of marketing apps has created a new divergence in lightweight, usable tools to deliver “microservices” for interactive content. And no, this isn’t an app like Instagram. Marketing apps are web-based and don’t require installation, can work on any device, and can be published or taken down at any time without the constraints of AppStore.
Not only do these marketing apps implicitly engage users, breed more enthusiasm, and feed users more memorable information, but they also supply brands with the very data that allows them to know their customers on a more personal level. If you score wrong on a quiz, it tells marketing what you don’t know. If you calculate your ROI, you are providing sales with the metrics of your business.
The stars of interactive content understand that it’s not all about the data, though. Vendors like Ion Interactive and Ceros allow marketers to create tools without any programming background. This eliminates cookie-cutter polls and quizzes, allowing them to customize their tools directly for their customers that they know and understand best.
Right now this means that active learning is intertwining with the data-based realism to deliver leads in more interactive ways. So what’s your excuse for not using them?
Paige DiPrete is a rising junior at Georgetown University studying Global Business and Portuguese. As an account service intern at gyro in Washington, D.C., she manages agency-client communication and researches MarTech insights.
by scott.gillum | Mar 31, 2016 | 2016, Marketing
Organizations are spending millions of dollars to “digitalize” themselves, as a way to become more agile and responsive to customer needs. As Gartner says, “Companies should be able to ‘react at Internet speed’ with real-time analytics to better understand individual buyers, and how to serve their unique needs.”
The payoff of these efforts is a more competitive and innovative organization that provides a consistent and engaging customer experience. As the organization become flatter and more transparent, it also brings a certain degree of risk. And, increasingly, that risk is falling on one group.
Yes, you guessed it: marketing.
According to HBR’s Designing a Marketing Organization for the Digital Age report, marketing is not only responsible for creating a consistent customer experience across the enterprise; perhaps even more challenging, it’s responsible for getting the organization to embrace change.
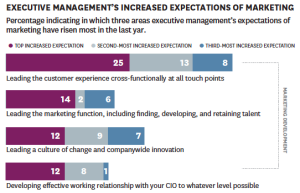
Ramping up the organization to operate at the new “Internet” speed of change is critical, according to McKinsey’s Cracking the Digital Code global survey. Forty three percent of executives surveyed said that high-performing digital companies go from idea to implementation in less than six months.
And let’s not kid ourselves about the herculean effort this may involve. Twenty five percent of executives who participated in the survey expressed concerns about their organization’s ability to keep pace, and its ability to adopt an “experimentation” mind-set required to make this transformation.
Marketing is, however, well equipped to take on the challenge; it has always advocated for customers and their experiences. Now it’s being empowered to take ownership of it across the entire enterprise. Marketing has long been the “tip of the spear” for digitalization, operating as the “hub” of digital interactions with customers for years. No other group has had to embrace and operate at the “speed of the Internet” like marketing has.
So it’s not surprising that 75 percent of marketers expect to be responsible for the customer experience, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit.
If marketers can successfully bring about the change needed to digitalize the organization, it should also yield additional organizational benefits that go beyond the customer experience. For example:
- Improving the culture. 89 percent of senior executives said that great companies build cultures that consistently create excellent customer experiences. Corporate culture also plays a critical role in attracting and retaining digital talent, according to McKinsey.
- Aligning customer service to the brand message. Although this has been discussed for years, companies are increasingly aligning the performance of customer service to brand health metrics, according to the HBR report. The Aberdeen Group also noted that when customer service is in sync with how marketing manages the brand, company revenues rises, as do social media mentions.
- A new organizational model. According to Frank van den Driest, author of The Global Brand CEO: Building the Ultimate Marketing Machine, in a digital world, marketing will evolve from expertise in “things” like television, ecommerce and media, to “thinkers” who excel at understanding and using data, “feelers” who are immersed in customer behavior and interaction, and “doers” who implement campaigns, creating content and measurement.
Given the importance of this digital transformation, improving the customer experience is now the No. 1 CEO expectation of their chief marketing officer, according to Gartner. For years, marketers have been asking for a seat “at the table,” and now they have it…and it’s a hot one.
 There is a grocery store a few miles from my house. It’s small and older, at least thirty years in its current location. Usually, the shelves are poorly stocked with a limited selection compared to the newer stores surrounding it. Despite these facts, the store manages to stay in business which is somewhat hard to comprehend given the cut throat, low margin nature of the industry. It survives because it has a secret weapon.
There is a grocery store a few miles from my house. It’s small and older, at least thirty years in its current location. Usually, the shelves are poorly stocked with a limited selection compared to the newer stores surrounding it. Despite these facts, the store manages to stay in business which is somewhat hard to comprehend given the cut throat, low margin nature of the industry. It survives because it has a secret weapon.








