by scott.gillum | Jul 29, 2015 | 2015, Observations
This year’s Fortune Brainstorm Tech conference in Aspen was an incredible experience.
 There were fantastic insights dropped by speakers like Rahm and Ari Emanuel, John Doerr from Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers, Reid Hoffman, CEO of Greylock Partner and co-founder of LinkedIn. I came away from the two and half-day event with three “ah-ha’s” because of their potential impact as game changers for marketers.
There were fantastic insights dropped by speakers like Rahm and Ari Emanuel, John Doerr from Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers, Reid Hoffman, CEO of Greylock Partner and co-founder of LinkedIn. I came away from the two and half-day event with three “ah-ha’s” because of their potential impact as game changers for marketers.
The New Native Advertising
Consumers are interacting with brands nearly all of the time. In the past, no one was watching and no one really cared, but new digital platforms and big data companies are about to change that. Companies like Storehouse, are giving consumers a platform to tell and share their story, many of which involve brands. Organizations like Ban.jo are capturing those moments and are beginning to alert brands. This “new native advertising” will grow out of naturally occurring brand experience that quickly get amplified and shared with others — real people, experiencing real brands, in real time. As this trend evolves, look for the role of the agency to shift from that of being the creator of disruptive ads aimed at getting your attention to amplifier and distributor of consumer generated organic ads.
Smart Carts
Jet.com recently launched to bring club discount shopping online. Its innovative business model is built off of the “smart cart.” As consumers fill up their cart, the price of the items begins to change based on availability of the item and the shipping location. Jet.com sources items from small business and tries to fill orders from local merchants. For example, you buy a baseball and a bat; you’ll get one price, add a baseball mitt and it will change the price for all three items depending on what type of mitt you are buying. To get the best price, wait a couple of days for shipping. Buy it immediately, and you’ll pay another price. Jet.com promises savings of 10-15 percent by using the advantage of filling orders locally and then passing the shipping cost savings along to the consumer.
The Internet of Things
Connected cars are coming. Actually, you could argue that it arrived years ago with GM’s OnStar. The next evolution later this year will include apps, beacons and commerce platforms like Visa Checkout and Apple Pay. Order a pizza from the Pizza Hut app on the screen in your car and payment processes automatically. Pull into the specially marked space in front of the restaurant and a beacon alerts them you have arrived for pickup. It also verifies your identity confirming payment. As beacons and autos unite, companies must begin to find ways for that 5-8” screen in your car to be the next big opportunity for advertising. 
The most mind-blowing thing I saw or heard, though, is Ban.jo. Founded by Damien Patton, the company is what Inc. magazine describes as the “The Most Important Social Media Company You’ve Never Heard Of.” Ban.jo, by mining social media, can figure out what is happening anywhere in the world in real time by looking at a specific place at a specific time. Ban.jo was the first to detect the Boston Marathon bombing, the Ukrainian plane downing and even the Amtrak train wreck in Philadelphia. According to Patton, they beat traditional media organizations to the story by eight minutes on average.
Here’s the mind-blowing part: Ban.jo has built a virtual grid of more than 25 billion squares as an overlay of the entire globe. Their software monitors geo-located social posts for anomalies and then flags them for further investigation. It is, as Damien describes, “a crystal ball.” For marketers, it presents an opportunity to help facilitate the new native advertisement I mentioned above.
 Overall, the event was one of the most insightful conferences I’ve ever attended. From the location (Aspen) to the speakers, the event had a certain energy unlike any other event. It could be because of the amount of start-ups and investor present, but I believe it came from the attendees themselves. I met interesting people from fascinating companies who had a shared goal of meeting people and gaining knowledge. If you have the opportunity, put this in your budget for next year and book this event. I highly recommend it
Overall, the event was one of the most insightful conferences I’ve ever attended. From the location (Aspen) to the speakers, the event had a certain energy unlike any other event. It could be because of the amount of start-ups and investor present, but I believe it came from the attendees themselves. I met interesting people from fascinating companies who had a shared goal of meeting people and gaining knowledge. If you have the opportunity, put this in your budget for next year and book this event. I highly recommend it
by scott.gillum | Mar 2, 2015 | 2015, Marketing
For business, this is turning out to be the “year of the human.” Andy Goldberg, global creative director at GE, said in an interview with Advertising Age about marketing trends in 2015: “We need B-to-B to be more human.” Karen Walkers, SVP of marketing at Cisco, went ever further by saying, “Devotion to brands begins and ends with an emotional connection. Buyers are people, people are humans and humans are emotional beings.”
Why this sudden awakening of humanity in tech marketing? The recognition that business decision makers are also people with emotional needs? Well, the answer might surprise you, and it’s based on a good bit of data and research.
The CEB (formerly Corporate Executive Board) first picked up on this trend in their research that found communicating business value (functional benefits of a product or service) was not differentiating because perceptions on that value h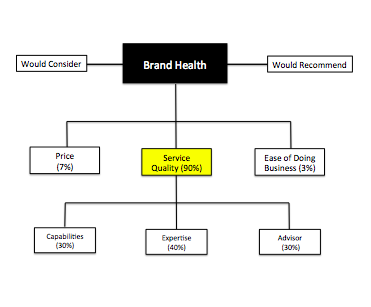 ardly varied between brands.
ardly varied between brands.
For example, a recent brand health study for a tech client found that 90 percent of their brand health (defined by a willingness to recommend and consider) was driven by service quality. Service quality made up 90 percent of the attributes in the graphic.
The smart marketer would think that in order to improve our brand health, we should increase our focus and communication for the performance attributes related to service quality. And they would be right, except for the fact that those business value drivers also apply to all competitors in the category, which is apparent in the graphic below:
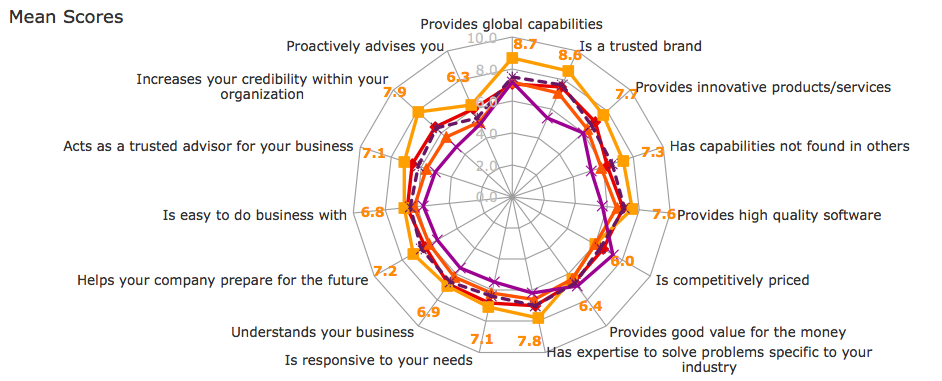
Each color line represents how a competitor scored on performance attributes under capabilities, expertise and strategic advisors. It is almost impossible to distinguish between the five companies represented (except for the competitor in orange, which also happens to have a leading share of market, mind and voice).
What is clear from the research is that rational purchase drivers that communicate business value, although important, are nothing more than “table stakes.” So what creates separation?
The answer: An organization’s ability to build and communicate value based on the understanding of the risk/reward dynamic involved with a purchase decision. The reason: There is a direct correlation between the level of risk and the emotional involvement of the buyer. The higher the risk, the more emotions play a role. Technology purchases are a particularly high risk because they support critical functions within an organization from payroll to customer communications and more.
As a result, personas need to go deeper into understanding the emotional state of buyers as they go through the buying process. Marketers should map the mental state before, during and after the purchase decision, noting the emotions that buyers might be feeling at that time. Here are some key questions to consider as you go through this process:
- What challenge(s) does this purchase decision present for the buyer? It will defer if the buyer is new versus existing. As a marketer, it’s crucial to know how it’s different.
- What personal risks are at stake for this decision maker? Could they lose their job if they make the wrong decision? Invest in understanding their role and their challenges.
- What are the personal rewards for the buyer? Consider how the decision will pay off for them personally. Most often this will be career oriented, but not always.
It’s also important to note that buyers will already have preconceived feelings towards your brand. This may be a benefit or another hurdle to overcome. Our research in partnership with the FORTUNE Knowledge Group found that nearly two thirds of C-level executives said they believe subjective factors that can’t be quantified (including company culture and corporate values) increasingly make a difference when evaluating competing proposals. Only 16 percent disagree. Furthermore, 70 percent believe that a company’s reputation is the most influential factor when deciding what company to do business with.
Buyers trust their gut to make the right decision based on how they feel about a product and/or brand more than we think (and definitely more than we communicate). They make purchase decisions based on emotions, and then justify them with the business value drivers. It’s the emotional connection that triggers the decision and feature/functionality to support it, not the other way around.
What company does this best? It’s Cisco. Research has shown that they are the most emotionally connected customers. Not surprisingly, as Karen Walkers points out, Cisco recognizes that buyers are not just decision makers with budgets, but rather people who are emotional beings.
by scott.gillum | Jan 4, 2015 | 2015
It’s the time of the year to look back over the last 12 months and create a “best of” list. This year I’ve pulled the most popular posts from five different sites; Adage, Business2Community, Forbes, Fortune and LinkedIn. In addition, I’ve thrown in a few other noteworthy nuggets from the year at the end of the post.
Adage – Why Apple Pay Could be Huge, And It’s Not What You Think explored the potential upside of Apple Pay as an advertising platform. It sparked the most conversation, and debate, on Twitter. Time will tell if they this strategy will come to fruition.
Business2Community – 5 Key Tips and Da ta Points to Defend You 2015 Marketing Budget. The last post of the year required the most man hours, and it was the most reposted story of the year. It offers marketers help with their 2015 planning activities in the form of free research and benchmark data.
ta Points to Defend You 2015 Marketing Budget. The last post of the year required the most man hours, and it was the most reposted story of the year. It offers marketers help with their 2015 planning activities in the form of free research and benchmark data.
Forbes -the most popular and shared post of the year, Could Falling Test Scores Be a Good Thing for the US? explores the link between test scores and success in business. It also highlights the risk associated with over emphasizing left brain analytic skill development, outlined by Sir Ken Robinson in his Ted Talk video Do Schools Kill Creativity? The endorsement of Marc Andreessen certainly played a big role in the popularity of the post.
Fortune – Are Marketers Measuring the Right Things was the first post I wrote for our new partnership with Fortune. It profiles the efforts of Ciena, a networking company, to elevate marketings role, and importance, within the organization. The post highlights an unique survey tool used to gather feedback from the sales organization on the performance of marketing (see the dashboard below).
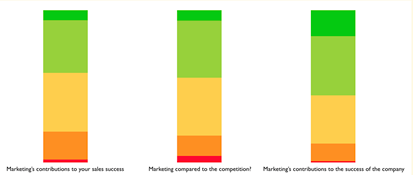
LInkedIn – 2014 marked my first year publishing on LinkedIn. Based on my experience so far, I’m not convince it will viable platform for content unless it becomes better policed. Too much promotional material seems is making its way on to it. At this point, I’m not sure I’ll continue to post.
That said, the most popular post on LinkedIn was also one of the most popular on Adage. The Keys to Differentiating Your Company From Others provides tips on how marketers can humanize their corporate brand to better resonate with audiences. It also identifies one of the common flaws of B2B communication – thinking that what you sell…is who you are. Hopefully, it also helped generated a new client for a follower.
Bonus Stuff
A couple of other noteworthy happenings from the year.
Moving on up.
The Next Generation of Apps Will Be All About You post that ran on Advertising Age was reprinted in the Sept/Oct version of The Portal magazine, a bi-monthly publication produced by the International Association of Movers.
 Taking Center Stage
Taking Center Stage
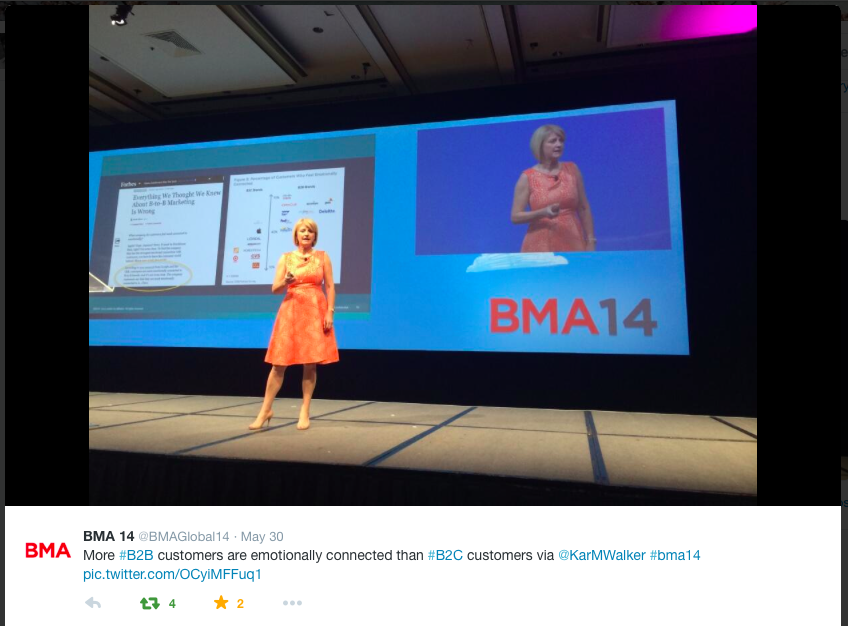
Karen Walker, SVP at Cisco, highlighted my post Everything We Thought We Knew About B2B Marketing is Wrong in her presentation at this year BMA member meeting in Chicago. The post now has close to 70,000 views.
Happy New Year! Here’s to an exciting year to come.
by scott.gillum | Aug 5, 2014 | 2014, Sales
The team killed it. The presentation was flawless. The proposal was outstanding. You covered all of the bases, but you lost. Searching for answers, the only thing you can think of is that the other guy must of “bought the deal,” right? In the article entitled; Why B2B Sales Leads Don’t Convert (and Who Is to Blame) Marketing Profs.com highlights a recent survey of close to 200 marketers, sales professionals, and president/CEOs on their thoughts on why deals were “lost.” Not surprisingly, 60% said that “price” was the main reason, but what may surprise you is that percentage is wrong. 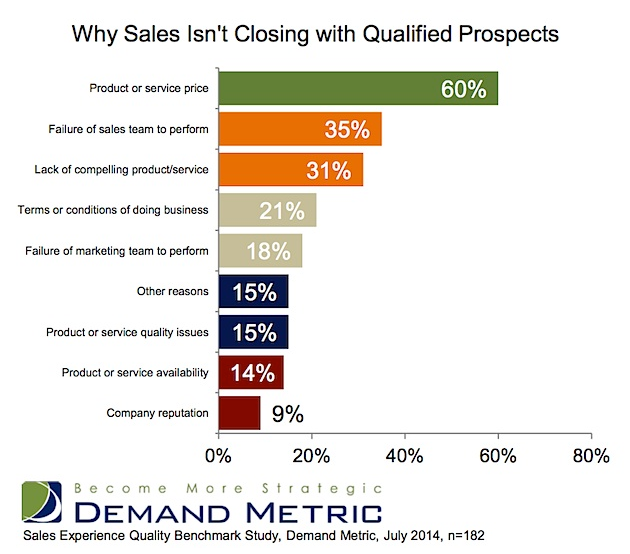
To truly understand why deals are lost, you have to get feedback from buyers. Having conducted numerous post mortem analysis of lost deals, and buyer behavior research, here’s what I have learned. Roughly one third of all buyers consider price as one of, or the main driver of a purchase decision. Pure price buyers represent about 5-10% of all decision makers. The remaining portion (20-25%) are value buyers who may, but don’t always, buy the lowest priced product or service. Using those numbers, the research overstates “price” as the reason for a loss by a factor of 2X. What accounts for the remaining thirty percent? Here are three common reasons for losing a deal, that doesn’t involve price.
- Low investment in the relationship – deals are not solely rationally made purchase transactions, especially as price and product complexity increases. Selling bigger ticket items involves a degree of trust built between a vendor and a buyer. Recent research by Fortune and gyro found that 65% of executives believe subjective factors that can’t be quantified (like a company’s culture and values) make a difference when evaluating competing proposals. Even more executives (70%) said that a company’s reputation was a critical consideration in the decision making process. Investing in relationship building with buyers takes time but as the research shows, it’s worth it. If buyers say that the only time they hear from a rep is when he/she wants to sell them something…that investment is not being made.
- Focusing on the wrong message – focusing on only selling the business value (functional benefits, business outcomes) of a product limits sales ability to make the case for a higher price. Connecting the value the product delivers to the buyer, on a personal level, helps reps broaden the conversation. According to CEB research, not only are you twice as likely to win the deal by focusing on personal value drivers
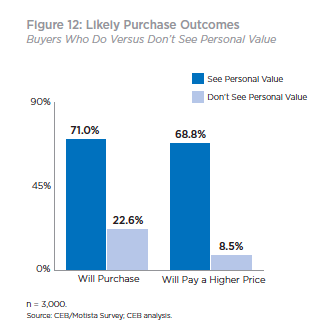 (professional and personal benefits, like a promotion, admiration from peers, etc.), but also, buyers are eight times more willing pay a premium. To do this effectively sales people need to be able to put themselves in the shoes of decision mak ers. They need to understand their buyers’ situation, role, relationships, etc., and sell the value of the product or service to those unique needs. If reps only know how to sell “feature functionality” the conversation will all too often come back to price.
(professional and personal benefits, like a promotion, admiration from peers, etc.), but also, buyers are eight times more willing pay a premium. To do this effectively sales people need to be able to put themselves in the shoes of decision mak ers. They need to understand their buyers’ situation, role, relationships, etc., and sell the value of the product or service to those unique needs. If reps only know how to sell “feature functionality” the conversation will all too often come back to price.
- Missing the real buyer – there is no guarantee that past buyers will be key decision makers in future purchase decisions, or on other types of products. Years ago, I did a post mortem analysis for a medical equipment company on an innovative new product. Sales said they were losing deals because it was priced too high. The analysis proved that they were both right, and wrong. The traditional buyer, did in fact, believe that the product was priced too high compared to others in the market. But a new set of users who had become the primary decision makers had emerged. This group was using the innovative technology as a revenue generating procedure. As a result, they valued the product differently and were willing to pay a premium. Deals were lost because the company didn’t understand how buyers intended to use the product, and as a result, they missed the key decision maker.
The simple answer is that deals are lost because the case for the value of the product or service has not been adequately expressed to meet the needs (professional, personal or both) of the key decision maker. Blaming “price” is a convenient crutch that shifts accountability to the product or pricing team, and away from sales and marketing. Finger pointing may make us feel better about our role, but it doesn’t fix the problem. If you are truly intent on increasing win rates dig deeper into understand why, I can guarantee you won’t find that it is “price” 6 out of 10 times.
 There were fantastic insights dropped by speakers like Rahm and Ari Emanuel, John Doerr from Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers, Reid Hoffman, CEO of Greylock Partner and co-founder of LinkedIn. I came away from the two and half-day event with three “ah-ha’s” because of their potential impact as game changers for marketers.
There were fantastic insights dropped by speakers like Rahm and Ari Emanuel, John Doerr from Kleiner Perkins Caufield & Byers, Reid Hoffman, CEO of Greylock Partner and co-founder of LinkedIn. I came away from the two and half-day event with three “ah-ha’s” because of their potential impact as game changers for marketers.
 Overall, the event was one of the most insightful conferences I’ve ever attended. From the location (Aspen) to the speakers, the event had a certain energy unlike any other event. It could be because of the amount of start-ups and investor present, but I believe it came from the attendees themselves. I met interesting people from fascinating companies who had a shared goal of meeting people and gaining knowledge. If you have the opportunity, put this in your budget for next year and book this event. I highly recommend it
Overall, the event was one of the most insightful conferences I’ve ever attended. From the location (Aspen) to the speakers, the event had a certain energy unlike any other event. It could be because of the amount of start-ups and investor present, but I believe it came from the attendees themselves. I met interesting people from fascinating companies who had a shared goal of meeting people and gaining knowledge. If you have the opportunity, put this in your budget for next year and book this event. I highly recommend it
 ardly varied between brands.
ardly varied between brands.
 ta Points to Defend You 2015 Marketing Budget
ta Points to Defend You 2015 Marketing Budget











