by scott.gillum | May 17, 2016 | 2016, Marketing
 One morning a couple of months ago I got in the car and my phone said travel time to my office 20 minutes and traffic was normal. A new feature of iOS9 is the ability for Apple Maps to detect when you enter your car by syncing with Bluetooth. I didn’t find it invasion, in fact, living in one of the worst cities in the country for traffic, I welcomed the information.
One morning a couple of months ago I got in the car and my phone said travel time to my office 20 minutes and traffic was normal. A new feature of iOS9 is the ability for Apple Maps to detect when you enter your car by syncing with Bluetooth. I didn’t find it invasion, in fact, living in one of the worst cities in the country for traffic, I welcomed the information.
Now that I’ve had a taste of IoT and “things connecting to things” I want more, and it’s given me a glimpse of what the future of mobile advertising might look like. Ads will go from being disruptive to being useful, perhaps even helpful. Mobile devices will become your digital doppelgänger signaling to other devices your presence, preferences and patterns.
For example, I’m on my way to LA for a meeting. My United app holds my flight itinerary, terminal and gate, Google/Apple Maps knows my current location, and my Starbucks app knows my buying behavior. My phone holds my intent, location and past purchasing history that could trigger opportunities to give me promotional messages as I journey to my gate.
Given the early morning departure, I’m in desperate need of coffee. The wall-mounted screens on the “people mover” (in the future) could flash me offer as I pass, inviting me to stop at a convenient store location by my gate. In this new world, my order would be ready and waiting for me when I arrived. Being between two locations, and missing the closest one, I would of appreciate this information as I have no time to backtrack.
Here’s the point — we are quickly moving to the ultimate marketing goal of getting the right message, to the right person, at the right time, and in the right place. But to enable this future, which will be data driven and permission based, the challenge for marketers is — how do we enbable it and/or keep from screwing it up?
Here are four things to consider:
- Retargeting – we have to stop being “creepy” by being better at targeting and knowing when to turn the “switch off.” Enough said on this topic, I think we all know the issues. Trying to be “personal” without having a relationship will get you into trouble.
- Overemphasizing Acquisition – IAB reported that digital advertising increased by 20%, and mobile by 66%, in 2015. Yes, there are certain elements of digital that deserve the investment, but attribution issues still exist. Take a hard look at your revenue mix and understand the most productive lead sources. Place your bets on improving conversion metrics, not just increasing volume. Don’t create a bunch of unnecessary noise at the top of the funnel.
- Undervaluing Upsell, Cross Sell and Renewal – With a future built on “permissions” existing relationships are the perfect starting point. Invest in helping customers become better consumers by thinking for them. Reposition marketing activities from being interruptive to being helpful, innovative and informative. Proactively reach out to them with offers based on their behaviors, focusing on how it will help them in their role, and not necessarily how it directly benefits your organization. Trust me, it will come back to you.
- Scrutinize Technology Investments – ChiefMarTech estimates that there are now over 3500 MarTech providers. It’s a “killing field” as Larry Ellison once described it. Over the next 2-3 years companies will either 1) run out of money, 2) merge or 3) be acquired. Carefully consider and select partners that will help build new mobile platforms, capabilities and tracking. Invest the time to get to know their business/funding model, existing customer base, and account team.
In the near future, highly personalized ads will spawn in real time based on consumer’s intent and location… and they won’t just appear on devices. Let’s hope that point arrives soon. I really could of used that Grande Dark for the plane ride. Airline coffee may say it’s Starbucks, but it really doesn’t taste the same.
by scott.gillum | Mar 31, 2016 | 2016, Marketing
Organizations are spending millions of dollars to “digitalize” themselves, as a way to become more agile and responsive to customer needs. As Gartner says, “Companies should be able to ‘react at Internet speed’ with real-time analytics to better understand individual buyers, and how to serve their unique needs.”
The payoff of these efforts is a more competitive and innovative organization that provides a consistent and engaging customer experience. As the organization become flatter and more transparent, it also brings a certain degree of risk. And, increasingly, that risk is falling on one group.
Yes, you guessed it: marketing.
According to HBR’s Designing a Marketing Organization for the Digital Age report, marketing is not only responsible for creating a consistent customer experience across the enterprise; perhaps even more challenging, it’s responsible for getting the organization to embrace change.
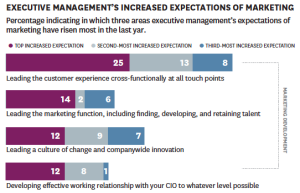
Ramping up the organization to operate at the new “Internet” speed of change is critical, according to McKinsey’s Cracking the Digital Code global survey. Forty three percent of executives surveyed said that high-performing digital companies go from idea to implementation in less than six months.
And let’s not kid ourselves about the herculean effort this may involve. Twenty five percent of executives who participated in the survey expressed concerns about their organization’s ability to keep pace, and its ability to adopt an “experimentation” mind-set required to make this transformation.
Marketing is, however, well equipped to take on the challenge; it has always advocated for customers and their experiences. Now it’s being empowered to take ownership of it across the entire enterprise. Marketing has long been the “tip of the spear” for digitalization, operating as the “hub” of digital interactions with customers for years. No other group has had to embrace and operate at the “speed of the Internet” like marketing has.
So it’s not surprising that 75 percent of marketers expect to be responsible for the customer experience, according to the Economist Intelligence Unit.
If marketers can successfully bring about the change needed to digitalize the organization, it should also yield additional organizational benefits that go beyond the customer experience. For example:
- Improving the culture. 89 percent of senior executives said that great companies build cultures that consistently create excellent customer experiences. Corporate culture also plays a critical role in attracting and retaining digital talent, according to McKinsey.
- Aligning customer service to the brand message. Although this has been discussed for years, companies are increasingly aligning the performance of customer service to brand health metrics, according to the HBR report. The Aberdeen Group also noted that when customer service is in sync with how marketing manages the brand, company revenues rises, as do social media mentions.
- A new organizational model. According to Frank van den Driest, author of The Global Brand CEO: Building the Ultimate Marketing Machine, in a digital world, marketing will evolve from expertise in “things” like television, ecommerce and media, to “thinkers” who excel at understanding and using data, “feelers” who are immersed in customer behavior and interaction, and “doers” who implement campaigns, creating content and measurement.
Given the importance of this digital transformation, improving the customer experience is now the No. 1 CEO expectation of their chief marketing officer, according to Gartner. For years, marketers have been asking for a seat “at the table,” and now they have it…and it’s a hot one.
by scott.gillum | Feb 28, 2016 | 2016, Marketing
 Having a hard time convincing “the powers that be” to invest in the brand? Ever wonder why it’s so hard, why all they want from marketing is leads? Let me explain.
Having a hard time convincing “the powers that be” to invest in the brand? Ever wonder why it’s so hard, why all they want from marketing is leads? Let me explain.
In organically grown companies, an organization develops a product or service and goes to market through a sale channel, either owned or via a partner. At this point, the organization is focused on acquiring customers and generating revenue. With low market awareness the organization typically has more sales capacity than demand for its products or services.
If marketing exists, it’s in its infancy, and plays a tactical role developing sales material, supporting business development activities, and it may have a small social media presence.
To fuel the company’s growth, the management team begins to realize in order to make sales and revenue objectives it has to be able to create demand beyond what the sales channels can generate on its own. As a result, marketing expands beyond its most basic sales enablement role into being responsible for generating leads.
When growth slows and/or begins to plateau, the executive management team will (or should) begin to explore the value of “strategic” marketing. Unfortunately, these strategic marketing activities and investments aimed at broadening awareness of the brand are often misunderstood and/or dismissed all together. Here’s why they shouldn’t be, and why they are critical to unlocking a company’s next phase of growth.
Why it’s so hard getting to “Yes”
The challenge in convincing the organization that marketing can be a strategic growth level is one of perception. Because marketing evolves “bottom up” as I just described, the common perception among executives is that marketing is a “tactical support” function.
The second issue is the messenger. The staffing needs of marketing in its infancy are simple, and usually satisfied by an entry-level hire or someone without a marketing background. Rarely, will this person rise to a senior management level. Achieving senior executive “gravitas” is critical for changing perception among the senior management team, especially if the company has a strong sales and/or product culture.
How to win the battle
To convince executives, you have to tie brand investments back to something “tangible.” Your argument has to show a direct connection to an organizations performance, be it sales, profit or the customer. And, if you can improve your message, you will also improve how your executives view the messenger. Here are three areas to explore.
- A strong/valued brand lifts price point. Are reps constantly complaining about being beaten up on regarding cost/price? A company that has a strong brand can command a price premium. Years ago, I did some work with competitor of Cisco and found that the Cisco brand had a price premium of 7% over the competitors. Why? B2B purchases are high risk, and as a result, are emotionally charged. Buyers that connect personally to brands are willing to pay more for their product if they believe it will reduce the risk of a bad decision. Need proof, click here.
- Improving top of the funnel performance improves the performance of the entire pipeline. Need to increase leads? You have two choices, expand the top of the funnel, or increase conversation rates. The best solution is to do both. By expanding the number of prospects aware of your product you increase the number who will also consider it, which increases the number of opportunities, leads and wins. If you only focus on increasing leads, you’re stuck with improving conversion rates, which may be much more difficult and/or costly.
- Brand building doesn’t mean you need a big budget. The fact is you’re doing it everyday, for better or worse. Every conversation a sales rep has with a prospect creates a brand impression, every unresolved service call to the contact center has the potential to damage the brand. You can make great strides by clearly and consistently communicating what the brand stands for both internally and externally. Once defined, put it into the language of your audience in the simplest terms possible. Complex, “consultant like” words and terms are meaningless. The really smart folks simplify the complex.
Now that you’ve made the argument, it’s time to close the deal. When an executive evaluates a proposal from your company against other competitors, do you know what tips the scale in your favor? No, it’s not price, or the “relationship,” it’s your reputation, your brand. It’s how they feel about your company…and that’s not in your proposal.
by scott.gillum | Jan 19, 2016 | 2016, Marketing
 Go ahead and get mad at me. Feel free to fill up the comment section below. I’m going to share our closely held secrets with sales people, skeptics and other critics of marketing. I know you would rather I not, but it’s best for all of us, trust me. Here we go…
Go ahead and get mad at me. Feel free to fill up the comment section below. I’m going to share our closely held secrets with sales people, skeptics and other critics of marketing. I know you would rather I not, but it’s best for all of us, trust me. Here we go…
#1 – You got lucky – if you generate leads off the first drop/wave of a new account acquisition or a lead generation campaign for a solution, you’re more likely to be lucky, than right. Yea, you may have had a compelling offer, and the call to action was intriguing, but the chances are, you just happened to hit a prospect at the right time.
Sure, in some industries you can buy data that identifies a company’s spend on certain products or services. But you don’t know if the budget is available, what portion of it, or who controls it. And since this is a prospect, you are most likely targeting a title, which could be a decision maker, a budget holder, or just a curious information seeker.
At the beginning of a campaign you simply don’t have the information on a prospect to know where they are, or how to advance them in the buying process. So, if a prospect does put their hand up and says, “Call me,” you most likely hit them at the right time in the buyers’ journey.
#2 – Your messaging is weak – the effectiveness of your message is being compromised by the fact that you are trying to motivate an audience to think or feel differently without explaining why. According to Pat Spenner, co-author of the new book entitled The Challenger Customer, marketers spend too much time focusing on how they want audiences to think, or feel, without understanding their current mindset.
Research for the book found that the receptiveness and/or openness to a message depends heavily on an audience’s existing belief system, which drives their behavior. According to Spenner, marketers first need to understand and break down the audience’s current mindset using insights about their business, customers, markets, etc. It’s an opportunity to “teach” audiences that their current thinking is no longer valid and why a new way of thinking is needed. If done well, the new mindset will uniquely lead them back to your product/services or brand.
For example, Merck developed the cholesterol-lowering drug Mevacor at a time when doctors knew little about the effects of cholesterol on the body. The current mindset was that hypertension (high blood pressure) caused heart disease. Merck used clinical research to show doctors the impact of high levels of cholesterol on arteries and the correlation of plaque buildup with coronary heart disease (the “teaching” moment).
As a result, doctors should test patient’s cholesterol levels to see if they are at risk. If a patient had a LDL cholesterol level above a certain point, doctors should start with a therapy regiment that included diet and drug treatment (the new mindset). The only cholesterol-lowering agent available at the time was, you guessed it, Mevacor. Merck, by getting doctors to change their mindset about the causes of heart disease, lead them back to their product. As Spenner puts it, effective story telling for marketers should “lead to, not with.”
#3 – You’re doing lead nurturing the wrong way – changing mindsets takes time. Yes, you’ve built prospect profiles, aligned content to their interest, and you may even know how to engage them in their preferred communication channel. The problem may not be your content marketing efforts but the fact that prospects are stuck in the status quo. They may find your information interesting, but it hasn’t convinced or motivated them to change their behavior.
Nurturing efforts should continue to break down, or build up, the new mindset across the buying group. The ability to drive specific information aligned to individual buyer’s needs may actually be causing more dysfunction within an already dysfunctional group. To advance a prospect/s refocus efforts on driving consensus on the issue and solution within the buying group. If done correctly, like Merck, prospects will come to own conclusions that you offer the best solution for their needs.
Motivating an audience to change doesn’t happen overnight. Unfortunately, marketers are under constant pressure to perform and rarely have the luxury of time to change their approach. It’s the reason I shared the first dirty secret, to buy marketers time to create the type of campaigns that deliver insights told as a story revealed over time.
The first wave of your campaign will generate leads, but it’s the waves that come after that really count. If marketers can stop telling customers why they need their product and let them come to that conclusion on their own, response and conversion rates will double based on my experience. But don’t tell anyone, it’s a secret.
by scott.gillum | Oct 5, 2015 | 2015, Marketing
 The Volkswagen scandal has already claimed the CEO. But could the damage also take down the company, or be the nail in the coffin for diesel automobiles in the US? Some are starting to think so: VW stock has fallen 30 percent since the scandal broke, and there are broader concerns about the impact on the reputation of Germany’s automobile industry. How could something that has the potential to be so damaging to an organization, and industry, happen?
The Volkswagen scandal has already claimed the CEO. But could the damage also take down the company, or be the nail in the coffin for diesel automobiles in the US? Some are starting to think so: VW stock has fallen 30 percent since the scandal broke, and there are broader concerns about the impact on the reputation of Germany’s automobile industry. How could something that has the potential to be so damaging to an organization, and industry, happen?
At some point, someone in the VW organization decided to cheat, and others within the organization approved that decision. And with that, it set in motion a chain of events that would reach across the organization. Someone designed the “defeat device” that could sense when the car was undergoing emission testing; another group tested the software to ensure it was working properly. Others submitted data to governing organizations using the deceptive and/or outright false data and so on (you get the picture, and it’s not pretty). VW’s corporate culture condoned this behavior.
“Big deal,” you say. “Things like this are probably going on in big global corporations all the time, all over the world. CEOs are out to win at any cost.” Not so fast. Research from the FORTUNE Knowledge Group and gyro found that sixty percent of executives prefer to do business with companies that are intent on doing what’s right, even when it doesn’t necessarily maximize revenue.
And don’t think that CEOs aren’t paying attention to a company’s reputation. When choosing a company to do business with, 70 percent of executives in the study cite company reputation as the most influential factor, with the company’s culture being the top driver of reputation, according to 53 percent of executives surveyed by FORTUNE and gyro.
Not only will VW take it on the chin from consumers – especially customers who own their diesel cars – but they are also going to feel the repercussion on the business side as well. Key decision makers, from suppliers to dealers, are going to be distancing themselves from the organization. This could potentially hurt the company’s ability to repair its reputation, which, according to a 2013 study by Deloitte, is the “number one strategic risk for large companies.”
The lesson: If you cheat, you will eventually get caught. Even though you may be able to avoid punishment (like a certain football player), you will not escape having your brand and reputation damaged. For some brands, that could represent up to two-thirds of the company’s value.
When an organization deceives us, they betray our trust and it’s deeply personal. It doesn’t matter if it’s a friend or a car manufacturer, our brains trust brands the same way we trust our friends, according to research from the Institute for Experimental Business Psychology at Leuphana University in Luneburg, Germany (of all places).
by scott.gillum | Sep 3, 2015 | 2015, Marketing
Just when we’ve convinced the organization that the key to our marketing communication success is personalized content, new research from CEB highlights that we actually may be doing more harm than good.
The years spent improving our understanding of the buyers journey, the development of more insightful personas and content, may have resulted in marketers ability to be too good at personalizing solutions to buyers. How can that be?
 The issue, according to CEB’s research underpinning their new book The Challenger Customer, is that our improved ability to increase a buyer’s awareness of those areas of a solution most relevant to them, has inadvertently increased visibility into the overall risks associated with the purchase decision and/or change. As a result, buyers begin to unbundle and simplify solutions, driving down price points. The shocker of this insight is that marketers improved ability to personalize content may be coming at a cost to sales.
The issue, according to CEB’s research underpinning their new book The Challenger Customer, is that our improved ability to increase a buyer’s awareness of those areas of a solution most relevant to them, has inadvertently increased visibility into the overall risks associated with the purchase decision and/or change. As a result, buyers begin to unbundle and simplify solutions, driving down price points. The shocker of this insight is that marketers improved ability to personalize content may be coming at a cost to sales.
According to co-author, Pat Spenner, the real challenge lies in convincing buyers to first agree on making a change. “Focus your content marketing efforts on creating a consensus case for change among the decision making group,” which according to CEB’s research, now involves at least five people in the typical B2B purchase.
According to Spenner, “personalization can hurt the buyer’s ability to get that critical early consensus, because it can cement those individual stakeholders into their individual contexts, without doing anything to bring that more diverse group together around a common vision for change.”
So should we stop personalizing our communication? No, but it does highlight the need to also create that common rallying point, and to equip key buying group stakeholders with the tools to create consensus around it. Something the authors say helps clients elevate the conversation from “me to we,” an umbrella approach that ties your content efforts together regardless of the audience being targeted.
To motivate buyers to change you first have to disrupt their status quo by planting and nourishing seeds of doubt about “business as usual.” Show them not just the benefits of action, but the consequences of inaction. CEB recommends using fact-based content built off a Commercial Insight to break down buyers existing mental models.
Concurrent with breaking down the audience’s long held beliefs, you need to give them something to aspire to — a new future state that rallies the group to take action. This is where a compelling creative campaign does the heavy lifting. A “big play” campaign, like IBM’s “Smarter Planet” creates a compelling future vision but also provides a broad platform to disrupt IBM’s many different buyers and to cover IBM’s expansive solution/product portfolio.
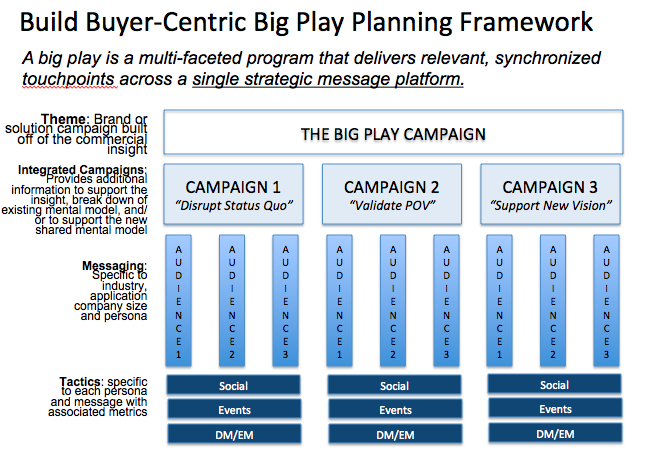
Personalization is still essential, and comes via messaging to specific audiences, but it is built on the commercial insight, and aligned to the common vision of the future state. It’s not that personalization doesn’t work, in fact, it can be very effective for breaking the status quo,” according to Spenner, “but you also need an unifying rallying point for buyers who may be too attuned to the risk associated with change.”
The key to leveraging the good work marketers have done to increase relevancy with buyers? Properly balance and/or convince the audiences that the rewards associated with making the change, both organizationally and personally, outweigh the risks you’re asking them to take on. If not, they will reduce the risk for you, and you may be hearing about it from sales.
 One morning a couple of months ago I got in the car and my phone said travel time to my office 20 minutes and traffic was normal. A new feature of iOS9 is the ability for Apple Maps to detect when you enter your car by syncing with Bluetooth. I didn’t find it invasion, in fact, living in one of the worst cities in the country for traffic, I welcomed the information.
One morning a couple of months ago I got in the car and my phone said travel time to my office 20 minutes and traffic was normal. A new feature of iOS9 is the ability for Apple Maps to detect when you enter your car by syncing with Bluetooth. I didn’t find it invasion, in fact, living in one of the worst cities in the country for traffic, I welcomed the information.




 The issue, according to CEB’s research underpinning their new book
The issue, according to CEB’s research underpinning their new book 





