by scott.gillum | Sep 15, 2014 | 2014, Tech Trends
Like much of the world I tuned in last week to watch Tim Cook unveil the latest Apple products and services. Afterwards, I was curious to see the analysts and so called “tech experts” reactions on the announcement. Most were ho-hum “nothing new here”, and “it was what we expected,” the market response was similar, with the stock getting a small bounce then falling after the announcement.
Apple, better than anyone, gets the “use case” right for its technologies. And it is why I was surprised by the media and analysts reaction. Listening to the announcement and recap, most of the focus on Apple Pay was on Retail use. In the press release, Apple discusses the near field communication (NFC) technology, names its retail, credit card and bank partners. Pointing out that there are merchants ready to accept Apple Pay as a very secure payment method. But nothing that really got the media excited, go into any Starbucks on any day and you will see plenty of mobile transactions.
Digging a little deeper, buried at the bottom of the announcement is something more intriguing – “Touch ID” which enables “one touch checkout” for Online Shopping Apps. Say good-bye to the hassle of entering your credit card information on the small screen. See something you like, touch it, and it’s yours!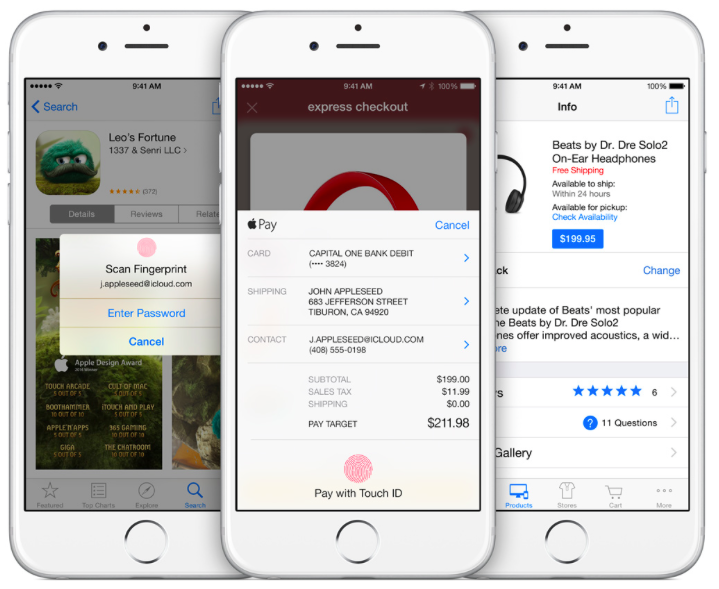
App developers have already started building Touch ID into retail apps. On the same day of Apple Live, Target announced that it has adopted the Like2Buy platform that which allow the chain’s Instagram followers to buy products featured in photos and Target is now integrating Touch ID into its mobile app. Touch ID for mobile apps is the big deal, but not for the reasons you might think.
Apple is a “big play” kind of an organization. A $349 watch, and people upgrading to an IPhone 6 isn’t going to move the needle for a $171 billion dollar company. Apple Pay helps but that’s a basis points play that gets split multiple ways between the service provider, credit card company, the bank, etc., and it will take years for it to be widely accepted. So where’s the “big play” with Apple Pay?
It’s mobile advertising. According to Mary Meeker in her 2014 Internet Trends report, mobile advertising represents a $30B opportunity in the US alone, based on time on device. Ad spend has lagged because of issues relating to tracking and measurability.
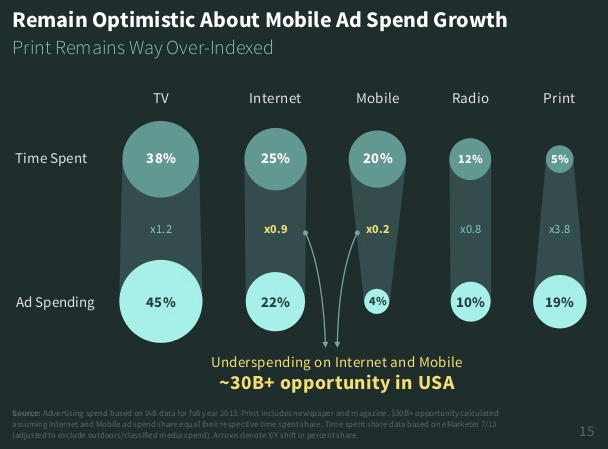
This is why Apple Touch ID is so important; it has the potential to improve tracking, measurability and ROI significantly. With TouchID the buyers never leaves the screen to transact. Attribution, tracking and conversion rates will improve, but the challenge remains — how do you get consumers to transact?
According to McKinsey’s From solutions to adoption: The next phase of consumer mobile payment, you give them a special deal or offer – an ad. There’s the closed loop.
Most important Drivers of Mobile Payments
Respondents ranking most important (light blue) and least Imports (dark blue)
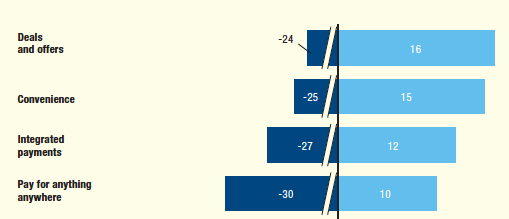
Apple has had a long history of introducing products at the beginning of the “hockey stick”, usually relating to the consumer adoption curve of new technologies, this time the hockey stick is mobile advertising. The real payoff of Apple Pay for now, in my humble opinion, is not retail, it’s mobile and it is about buying on your phone versus paying with your phone.
by scott.gillum | Aug 5, 2014 | 2014, Sales
The team killed it. The presentation was flawless. The proposal was outstanding. You covered all of the bases, but you lost. Searching for answers, the only thing you can think of is that the other guy must of “bought the deal,” right? In the article entitled; Why B2B Sales Leads Don’t Convert (and Who Is to Blame) Marketing Profs.com highlights a recent survey of close to 200 marketers, sales professionals, and president/CEOs on their thoughts on why deals were “lost.” Not surprisingly, 60% said that “price” was the main reason, but what may surprise you is that percentage is wrong. 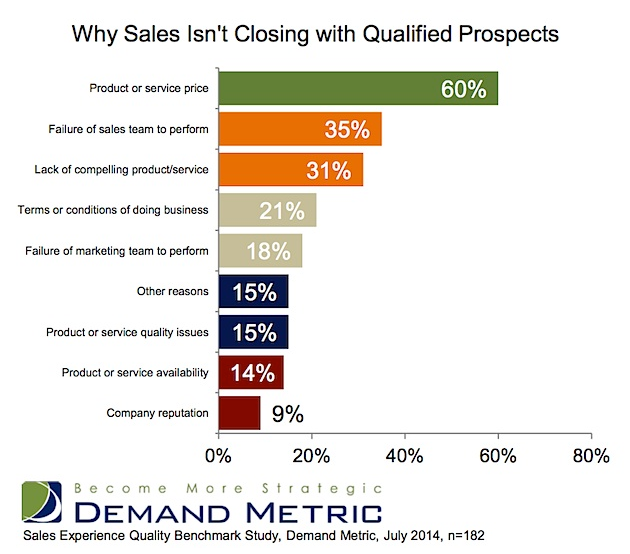
To truly understand why deals are lost, you have to get feedback from buyers. Having conducted numerous post mortem analysis of lost deals, and buyer behavior research, here’s what I have learned. Roughly one third of all buyers consider price as one of, or the main driver of a purchase decision. Pure price buyers represent about 5-10% of all decision makers. The remaining portion (20-25%) are value buyers who may, but don’t always, buy the lowest priced product or service. Using those numbers, the research overstates “price” as the reason for a loss by a factor of 2X. What accounts for the remaining thirty percent? Here are three common reasons for losing a deal, that doesn’t involve price.
- Low investment in the relationship – deals are not solely rationally made purchase transactions, especially as price and product complexity increases. Selling bigger ticket items involves a degree of trust built between a vendor and a buyer. Recent research by Fortune and gyro found that 65% of executives believe subjective factors that can’t be quantified (like a company’s culture and values) make a difference when evaluating competing proposals. Even more executives (70%) said that a company’s reputation was a critical consideration in the decision making process. Investing in relationship building with buyers takes time but as the research shows, it’s worth it. If buyers say that the only time they hear from a rep is when he/she wants to sell them something…that investment is not being made.
- Focusing on the wrong message – focusing on only selling the business value (functional benefits, business outcomes) of a product limits sales ability to make the case for a higher price. Connecting the value the product delivers to the buyer, on a personal level, helps reps broaden the conversation. According to CEB research, not only are you twice as likely to win the deal by focusing on personal value drivers
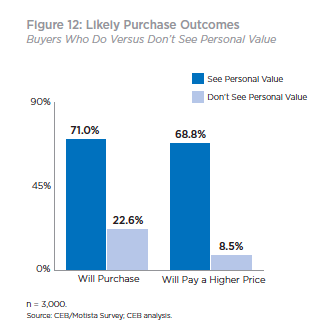 (professional and personal benefits, like a promotion, admiration from peers, etc.), but also, buyers are eight times more willing pay a premium. To do this effectively sales people need to be able to put themselves in the shoes of decision mak ers. They need to understand their buyers’ situation, role, relationships, etc., and sell the value of the product or service to those unique needs. If reps only know how to sell “feature functionality” the conversation will all too often come back to price.
(professional and personal benefits, like a promotion, admiration from peers, etc.), but also, buyers are eight times more willing pay a premium. To do this effectively sales people need to be able to put themselves in the shoes of decision mak ers. They need to understand their buyers’ situation, role, relationships, etc., and sell the value of the product or service to those unique needs. If reps only know how to sell “feature functionality” the conversation will all too often come back to price.
- Missing the real buyer – there is no guarantee that past buyers will be key decision makers in future purchase decisions, or on other types of products. Years ago, I did a post mortem analysis for a medical equipment company on an innovative new product. Sales said they were losing deals because it was priced too high. The analysis proved that they were both right, and wrong. The traditional buyer, did in fact, believe that the product was priced too high compared to others in the market. But a new set of users who had become the primary decision makers had emerged. This group was using the innovative technology as a revenue generating procedure. As a result, they valued the product differently and were willing to pay a premium. Deals were lost because the company didn’t understand how buyers intended to use the product, and as a result, they missed the key decision maker.
The simple answer is that deals are lost because the case for the value of the product or service has not been adequately expressed to meet the needs (professional, personal or both) of the key decision maker. Blaming “price” is a convenient crutch that shifts accountability to the product or pricing team, and away from sales and marketing. Finger pointing may make us feel better about our role, but it doesn’t fix the problem. If you are truly intent on increasing win rates dig deeper into understand why, I can guarantee you won’t find that it is “price” 6 out of 10 times.
by scott.gillum | Jun 23, 2014 | 2014, Marketing
I found this in a file earlier this week. It was part of a pre-work exercise for a well known professional services firm. We were engaged to help them redefine their corporate value proposition and messaging architecture. I thought it might be useful for the group.
Who Uses It?
Everyone:
- Marketing Teams
- Salespeople
- Recruiters
- Investor Relations.
What You Should Not Do:
Most elevator pitches miss the mark because:
- They are too long–“We have an elevator pitch but it requires a building with 700 floors…”
- They are too technical
- They lead with bragging points or product features — “We are the leading provider with 54 offices in 29 countries.”
- They are ego-centric rather than customer-centric—An elevator pitch is a response to the question what do you (or what does your company) do? When a customer asks this they mean, “what do you do for me? “
How To Do It Right:
- Be customer-centric
- Be concise (30-60 seconds max)
- Be true and “ownable”
- Convey business outcomes, not bragging points or features.
- Show, don’t tell— provide a story that will show a customer what your company will do for them.
Best Practices:
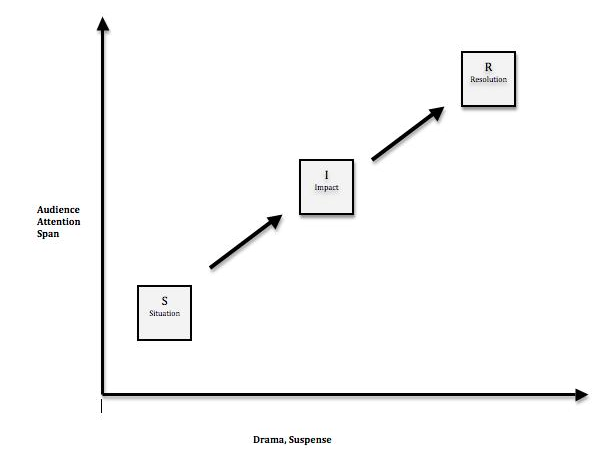
Elevator Pitch Should ‘Tell a Story’ that:
- Addresses: Situation, Impact and Resolution
- Starts with customers; ends with outcomes
- Quantifies your value proposition
Try beginning with a provocative statistic
It should consist of three parts:
- Situation – cite the dilemma, pain, difficulties or complications that the prospect faces…
- Impact – quantify the impact that the situation is having on the prospect’s bottom line…
- Resolution (Solution) – how do you solve the problem?
by scott.gillum | Jun 10, 2014 | 2014, Marketing
Tell me if you have heard this before; “we need more, and/or better leads.” The chances are, if you’re in hi-tech marketing you may hear it on daily, weekly and monthly basis. Why? According to Forrester consultant Tom Grant, it’s because of the need to feed the funnel.
In his report Tech Marketers Pursue Antiquated Marketing Strategies Grant compared hi-tech firms to other industries “B2B technology companies treat marketing as an opportunity to sell new products and services to new customers.” As he stated “the product is the axis around which marketing efforts turn,” and as a result, the primary objective of marketing is to produce leads.
Similarly, marketers have long held the belief that because of sales short-term focus on making quarterly objectives, it either lacks the appreciation of, and/or the sophistication to understand anything other than lead gen, for example longer-term brand building and awareness activities.
But what if both of these viewpoints were actually wrong. What would happen if you asked sales what they valued, rather than assumed you knew the answer? How might it change how marketing thinks about its impact on the organization?
For one B2B Tech Company, feedback from the sales force is helping them refine their value to the organization. “When it comes to enabling the sales force, we’ve previously relied on what I call “measurement-by-anecdote.” Our goal with this study was to quantify what sales values from marketing so we can focus on the things that make a difference.” said Rick Dodd, SVP Marketing of Ciena, a $2 billion global optical and packet networking company.
To gain that insight the company surveyed its global sales force, including five types of sales reps covering five different account types. Over 400 sales reps provided feedback on their priorities for marketing and marketing’s performance.
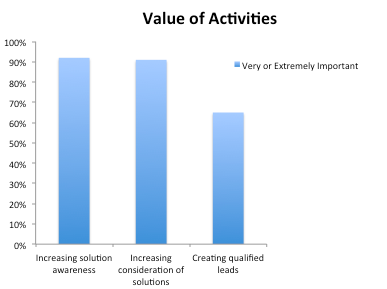
According to sales, the highest ranked marketing activities were at the top of the funnel, 92% of sales said that increasing the awareness of solutions was very or extremely important, increasing consideration was close behind at 91%, only 65% mentioned lead generation.
“Our sales force is very experienced; they understand that technology and industries change quickly. We’ve obviously been successful positioning ourselves for today’s market, and now we want to take best advantage of the big shifts in our landscape. The survey showed us that for sales to be successful, marketing has to be able to change customers and prospect perceptions,” according to Dodd.
Perhaps the most interesting insight to come out of the research, is how Ciena is now thinking about measuring and reporting marketing’s impact on the organization. “Measuring pipeline value is a struggle in our business”, said Bill Rozier, VP of Marketing. “We have long, complex sales cycles that make it difficult to isolate marketing’s impact.”And they are not alone it in that challenge. The Aberdeen Group’s recent Demand Generation study found that 77% of respondents rated visibility into lead performance across stages as very valuable, but only 43% indicated they can do thi effectively.
Instead of spending a lot of time and energy in trying to perfect an imperfect process, thecompany is focusing efforts on measuring marketing performance at the macro level. “At the end of the day, our performance is ultimately measured in sales success, so that’s what we are focusing on measuring”, said Rozier.
To do that, the company has created a quarterly dashboard from the survey. Two regional sales organizations each quarter will be asked to evaluate marketing’s performance in three areas: 1) Marketing’s contribution to sales success; 2) Marketing’s performance compared to competitors; and 3) Marketing’s contribution to the success of the organization.
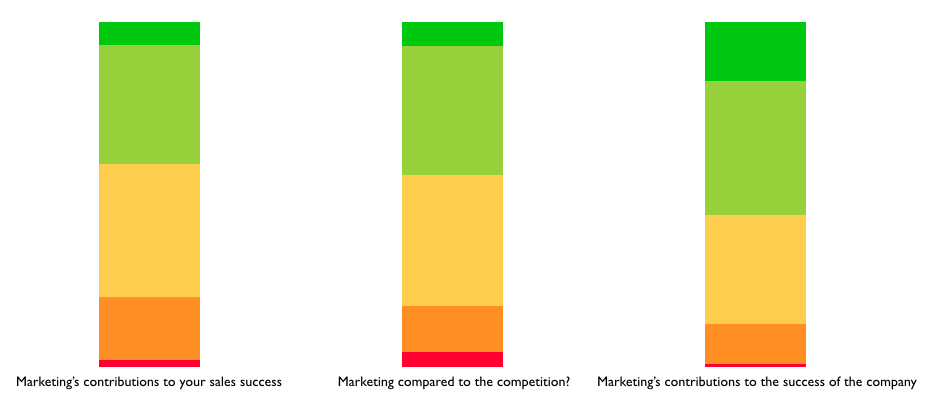
It’s a unique approach, and perhaps one that should be considered by others, because the challenge in performance management is often in defining the right metrics to drive the intended behaviors.
Ciena’s approach, as Dodd concludes, is to put the focus on the right conversation; “As we learned through the research, contributing to the success of the sales force isn’t just about one thing, it isn’t just lead gen. I appreciate that they give us credit for doing a good job when compared to competitors, but what we’re most interested in understanding is how well are we doing in enabling them to win. If the sales team rates our contributions as being valuable to their personal success, then we know we’re doing the right things.”
by scott.gillum | Jan 28, 2014 | 2014, Marketing
In December, I had the opportunity to be the Keynote speaker at the Bowery Capital CMO Summit in NYC. The event featured a number of high profile CMO’s speaking with an audience of mostly early stage startups (under 20 employees).
My presentation was based on the recent Forbes blog post Everything We Thought We Knew about B-to-B Marketing in Wrong. The audience also included some local media, a reporter from CMO.com wrote a summary of the speech.
http://vimeo.com/82457497














